Posted Date : 09 October 2025
Posted by : Ipseeta Dash
In today’s rapidly changing healthcare environment, non-invasive imaging has emerged as a transformative force, enabling doctors to visualize the human body's internal structures without the need for incisions or surgery. Whether it's identifying tumors early or monitoring a developing fetus, these technologies are now necessary in diagnostics, treatment planning, and medical research.
According to a 2024 report by Research Nester Insights, the global medical imaging market was valued at USD 39.1 billion and is expected to reach USD 62.8 billion by 2035, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1%. A significant portion of this growth stems from non-invasive methods, including MRI, CT scans, ultrasound, PET scans, and digital X-rays.
What Is Non-Invasive Imaging?
Non-invasive imaging refers to diagnostic methods that visualize the body’s internal structures without requiring skin incisions or the insertion of instruments. Unlike procedures such as biopsies or endoscopies, these imaging techniques depend on radiation, sound waves, or magnetic fields to assess detailed images of tissues and organs safely and painlessly.
Common Types of Non-Invasive Imaging Technologies
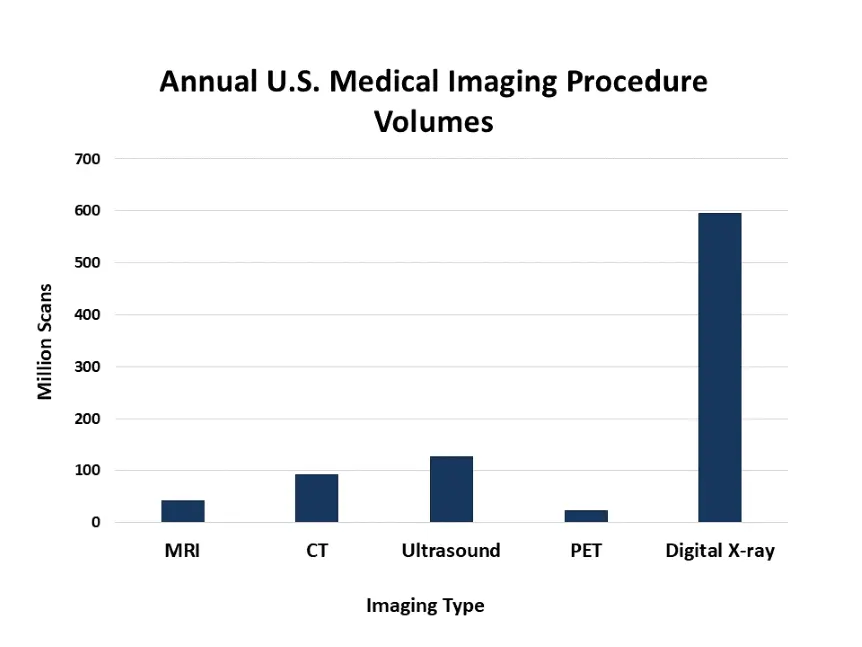
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce high-resolution images, especially useful for soft tissues like the brain, muscles, joints, and internal organs. One major benefit is that it does not include ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for repeated scans. According to the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), more than 36 million MRI scans are done annually only in the U.S. MRI helps to make out cases of Alzheimer’s disease, with studies predicting that 6.5 million Americans with 65 or above could benefit from MRI scans for early detection of dementia-related changes in the brain.
- Computed Tomography: CT scans capture multiple X-ray images from different angles to form thorough cross-sections of the body. Highly regarded for their speed and precision, CT scans are crucial in emergencies, such as stroke or trauma cases, and are also commonly used in cancer diagnosis and the evaluation of lung diseases. In 2022, about 91.6 million CT scans were performed in the United States (FDA), and in 2019, the usage rate was around 279 scans per 1,000 people, highlighting their widespread clinical use.
- Ultrasound Imaging (Sonography): Ultrasound requires high-frequency sound waves to create live images of internal organs. It is best known for its role in obstetrics, but it is also used for heart exams, i.e., echocardiography, abdominal scans, and even in musculoskeletal cases. The World Health Organization reports that, with more than 130 million ultrasound procedures performed annually worldwide, it is one of the most accessible and commonly used imaging tools. During pregnancy, ultrasound is used in all trimesters, with 57% of scans occurring in the second trimester. It also shows high accuracy in detecting kidney conditions, such as renal cysts (98%) and carcinomas (86%), based on clinical studies.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET): PET scans provide information about how tissues and organs function, rather than just showing their structure. This is done by injecting a radioactive tracer that marks the main active areas in the body. PET scans are often integrated with CT or MRI to detect cancer risks, track treatment response, and understand neurological or cardiac conditions. As per the National Cancer Institute, over 2 million PET scans are done annually in the U.S, making them highly essential for controlling cancer, Alzheimer’s, epilepsy, and coronary artery disease.
- Digital Radiography: X-ray imaging is one of the oldest and most commonly used diagnostic tools. It is fast, affordable, and credible for identifying bone fractures, dental issues, and lung conditions such as pneumonia and tuberculosis. According to the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), approximately 3.6 billion X-ray exams are performed worldwide each year. In Australia alone, 27.7 million people underwent diagnostic imaging, including X-rays, in non-hospital settings in 2022.
Each of these imaging technologies serves a different purpose in clinical settings. From detecting hidden tumors to assessing stroke damage or monitoring fetal development, non-invasive imaging helps physicians to make better decisions with less discomfort or risk to the patient. Together, these tools form the foundation of modern diagnostics, enhancing results through prior detection, better monitoring, and more personalized treatment approaches.
Applications Across Medical Specialties
Non-invasive imaging technologies have become indispensable tools across multiple medical disciplines, helping in accurate diagnosis and treatment without surgical risks.
- Oncology: MRI and PET-CT are important in detecting, staging, and monitoring cancers. MRI provides high-resolution imaging of soft tissues such as the brain, breast, and prostate, while PET-CT combines metabolic and anatomical imaging to identify cancer spread and treatment response. Early imaging detection can increase survival rates by up to 90% for several types of cancers, as per the American Cancer Society. With 2 million new cancer cases expected in the U.S. in 2024, imaging remains central to cancer care.
- Cardiology: Cardiology has also seen notable advancements through non-invasive imaging technologies. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly 48% of adults in the U.S. suffer from some form of cardiovascular disease. Non-invasive imaging is necessary in easing out early diagnosis and timely intervention, often before symptoms even arise.
- Neurology: Neurological disorders can be complex and life-changing, often hampering cognition, motor function, or emotional regulation. MRI and CT scans are essential for diagnosing strokes, brain tumors, multiple sclerosis, and neurodegenerative diseases. Functional MRI (fMRI) maps brain activity and assists in surgical planning. According to the Global Burden of Disease Study, neurological disorders contribute to approximately 10% of the global Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs). Hence, early and accurate imaging is necessary to improve the quality of life of patients with neurological illnesses.
- Orthopedics: CT and MRI help to analyze fractures, ligament injuries, and spinal issues. Musculoskeletal ultrasound offers a portable, real-time solution for diagnosing joint inflammation or guiding injections. These technologies speed up recovery and improve orthopedic surgery outcomes.
- Gynecology & Obstetrics: In gynecology and obstetrics, non-invasive imaging, especially ultrasound, has become a foundation of patient care. Ultrasound is foundational in prenatal care, used in over 90% of pregnancies worldwide. Obstetric ultrasound is necessary for monitoring fetal development, estimating gestational age, evaluating multiple pregnancies, and identifying anatomical abnormalities.
Technological Innovations Driving the Future
- Artificial Intelligence in Imaging: AI is changing medical imaging by enabling automated detection, segmentation, and diagnostics. The AI algorithms if trained on different cases, can identify abnormalities faster and more accurately than humans.
- Portable and Wearable Devices: Portable ultrasound and handheld devices such as Butterfly iQ are making diagnostics more accessible, even to rural and low-resource areas. Wearable MRI prototypes are being developed for real-time brain imaging, especially useful in epilepsy and sleep research.
- 3D and 4D Imaging: 3D imaging offers volumetric views that are highly necessary for surgical planning, especially in orthopedics and oncology. 4D imaging allows sophisticated monitoring, such as monitoring fetal movements or cardiac cycles.
- Hybrid Imaging Systems: Combining imaging modalities, such as PET-CT or PET-MRI, provides detailed anatomical and metabolic information simultaneously. These systems advance diagnostic accuracy and reduce the number of procedures a patient must go through.
Conclusion
As healthcare continues to move towards more patient-friendly, data-driven, and preventive approaches, non-invasive imaging technology stands at the forefront. It has already transformed diagnostics and treatment monitoring and is predicted to play an even greater role in personalized medicine, telehealth, and global healthcare equity.
Contact Us







