A Go-To-Market Strategy for International Businesses Entering the Indian Market
Maximizing Market Penetration & Customer Acquisition
Effective go-to-market strategies for entering the Indian market are essential for international businesses. Companies can optimize their market reach and attract customers by understanding the unique cultural and business environment.
Market Analysis in India
Key Demographics
India is the world’s most populated country, with over 1.45 billion individuals. The nation showcases a tapestry of demographics encompassing various age groups, ethnicities, and languages. Notably, a significant proportion of its populace comprises people with a median age of 28. This youthful demographic translates into a consumer market for various goods and services.
- GDP Growth Rate: According to the World GDP Ranking 2024 list, India’s current GDP stands at $3.95 trillion, showcasing a growth rate of 7.6% in Q2 FY24. India is currently ranked fifth in the world after the U.S., China, Germany, and Japan.
- Population: As of the end of April 2023, India surpassed China to become the most populated country in the world, with a share of 17.78% of the global population. Currently, the population of India is 1,450,935,791.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): India has been attracting significant FDI, with inflows reaching US $22.4 million in Q1 2024-25, surging by 26.4%. This has been the strongest growth in over 5 quarters. India had major FDI inflows during April 2000 to June 2024 with a 25% share (USD 168.85 billion) from Mauritius, 24% (USD 163.85 billion) from Singapore, 10% (USD 66.70 billion) from the U.S., 7% (USD 51.13 billion) from the Netherlands, and 6% (USD 42.54 billion) from Japan.

Market Size and Growth Rate
The Indian market is a prime landscape for business expansion given its substantial size, rising purchasing power, and burgeoning middle class. Notably, the middle class, essential for economic growth is projected to increase from 32% in 2020-21 to 63% in 2046-47. India’s purchasing power has seen a steady rise, reaching 23 LCU per international dollar in 2022 compared to 19 in 2003. Similarly, India’s GDP per capita recorded $2380 in 2022, indicating a growth of 6.70% compared to the previous year.
The middle class represents 31% of India’s total population and the graph is expected to hit 38% by 2031 and around 60% by the end of 2047. The expanding middle-and high-income demographics contribute to rising disposable income, allowing greater spending on diverse goods and services, thereby fostering a favorable environment for businesses in India’s consumer market.
Bengaluru emerged as the leading city in India for purchasing power among other cities, scoring 129 on the index as of July 2023. Credit access and higher incomes have been significant drivers in consumer behavior shifts. The credit card holders nearly doubled from 29 million in March 2017 to about 62 million in March 2021. As of September 2024, Pune emerged as a leading city in local purchasing power among other cities with an index score of 150, followed by Gurgaon and Hyderabad.
Consumer Behavior
Understanding India's unique purchasing habits, preferences, and demographic insights can help businesses tailor their approaches by targeting price sensitivity and value-seeking behavior and focusing on consumer’s local product preferences, sustainability, and digital shopping trends.
1. Purchasing Habits
According to a recent survey conducted in 2023, around 50% prioritize value for money while choosing a brand and follow price comparisons, discount hunting, and special offers before making any purchases. Moreover, the convenience of e-commerce and the availability of a wide range of products on several online platforms have resulted in rising online purchases, especially among millennials and Gen Z.
2. Preferences
Indian consumers have a wide range of preferences that are influenced by several factors including, culture, region, and income level. The majority of consumers value quality, authenticity, and personalized service and favor local products over international ones. Approximately 85% of India’s retail industry retail industry still relies on traditional stores, representing about 13-14 million outlets. However, there is a steady shift in buying patterns as consumers are realizing the importance of sustainability and social responsibility.
3. Demographics
India is home to a diverse range of people with different backgrounds, religions, languages, and traditions. Its diverse demographic landscape includes an expanding middle class that contributes to a greater purchasing power and makes consumer preferences highly varied. Millennials and Gen Z play a key role in shaping consumer trends, driven by social media influence and robust digital exposure. India has roughly 36.6% urban population with higher disposable incomes, advanced infrastructure, and access to a broader range of services and products.
Trading Scenario of India
India is seen to actively work on expanding its export portfolio to electronics, engineering products and services, pharmaceutical and food products apart from regular sectors such as iron ore and agricultural commodities. The Ministry of Commerce aims to enhance the export offerings by introducing alcoholic beverages, confectioneries, precocked meals, and value-added fruits such as jackfruits and bananas.

According to economic think tank GTRI data, China became India’s largest trading partner in FY 2023-24, surpassing the U.S with two-way commerce totaling USD 118.4 billion. The same analysis also states that India’s exports to China reached USD 16.67 billion, a notable increase of 8.7 percent in FY24 in sectors including iron ore, fruits and vegetables, cotton/yarn made-ups, spices, and plastic. Meanwhile, imports from China witnessed a rise of 3.24 percent, totaling USD 101.7 billion in high-tech gear such as telecom and smartphone parts, PCs, laptops, and plastic, steel, chemicals, and iron.

Key Industries Driving Indian Market
Key Sectors
The Indian economy is one of the fastest-growing sectors in the world, consisting of a range of high-potential sectors. Technology and IT services, e-commerce, healthcare, renewable energy, manufacturing, and agriculture are some of the notable sectors that provide opportunities for local and international businesses to expand, contribute to economic growth, and cater to the rising demand.
Industry 1: Information Technology
Information Technology (IT) sector in India contributes to approximately 8% of the country’s GDP and is projected to reach nearly 10% by 2026. This sector benefits from a skilled set of workforce and favorable government policies, making it a prime area of cloud computing, digital transformation, AI, and ML applications. Moreover, its strong IT foundation and business process outsourcing (BPO), position it for continued growth.

Industry 2: E-commerce
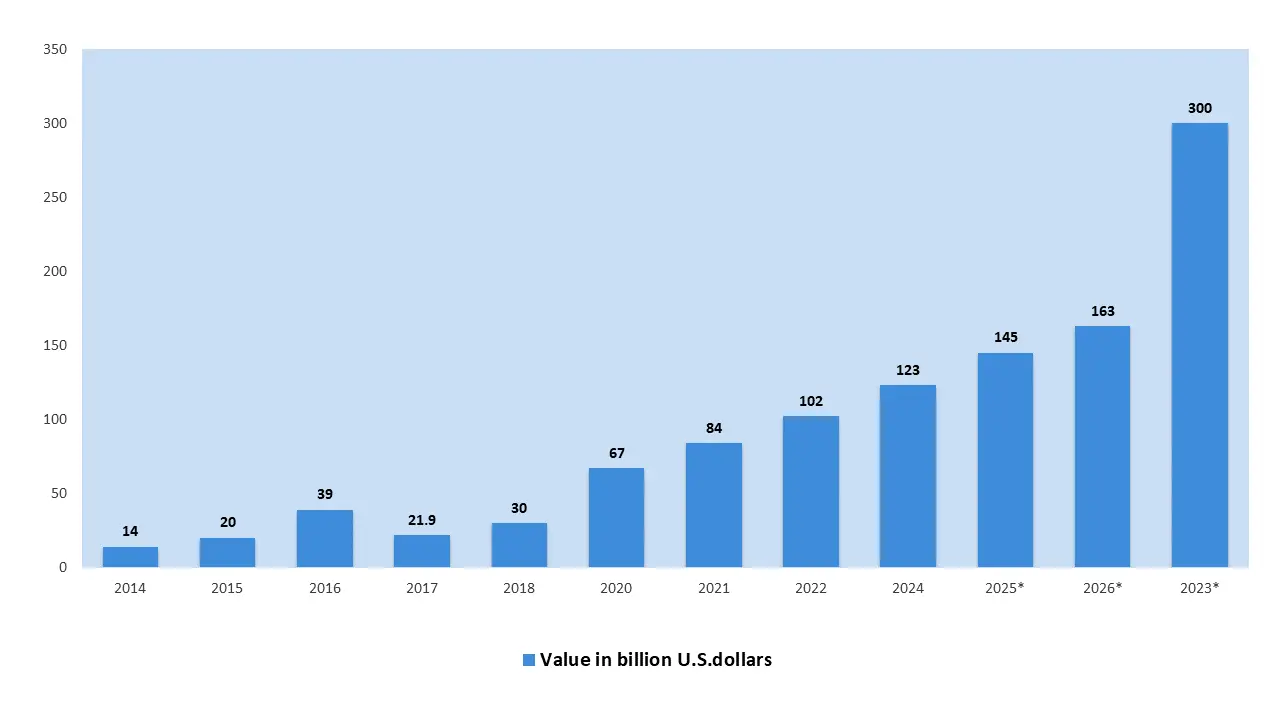
The e-commerce sector in India has witnessed rapid growth over the past few years. India currently ranks as the 7th largest e-commerce market across the globe, with revenue projections nearing $123 billion in 2024. The sector is growing owing to expanding internet access, high preference for online shopping, and rising usage of smartphones. E-commerce’s contribution to Indian GDP is expected to reach $300 billion by 2030. Prominent players such as Amazon, Flipkart, and Paytm Mall continue to shape the industry.
Industry 3: Renewable Energy
India possesses potential for growth in the field of renewable energy. Globally, India ranks third in renewable power capacity additions and contributes 5% of its GDP to renewable energy. The nation has established a goal of attaining a renewable energy capacity of 450 GW by 2030 comprising 280 GW from solar power 140 GW from wind power and 30 GW from bioenergy. This ambitious objective opens up prospects for investment and advancement, within the sector. The Indian government has put in place a range of incentives and policies to encourage the use of renewable energy. These include incentives like tax advantages, subsidies, and grants as well as regulatory steps to make it easier for projects to be developed and integrated into the power grid.
Moreover, the government has introduced initiatives such as the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) and the National Solar Mission to promote the expansion of solar power throughout the nation. India is currently witnessing the development of significant renewable energy initiatives. One remarkable project worth mentioning is the Rewa Ultra Mega Solar Park situated in Madhya Pradesh. This solar park is one of the largest in the world boasting a capacity of 750 MW. Spanning an area of 1590 hectares in the Rewa district, it has attracted substantial investments from domestic as well as international stakeholders. Additionally, Gujarat’s Kutch Solar Park stands as another endeavor with a capacity of 30 GW and aspires to secure its position as the world’s largest solar park.
Industry 4: Healthcare
The healthcare industry in India has experienced the fastest growth in recent years due to a large population base, rising healthcare expenditure, and a growing awareness of personal health and well-being. Health expenditures in India accounted for 2.1% of GDP in 2021-22. Over the two decades, FDI inflows in India have grown from $ 2.6 billion in 2000 to $ 52 billion in 2019-20. Furthermore, government initiatives such as Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY), Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM JAY), and improved access to facilities in rural areas have played crucial roles in driving India’s healthcare sector forward. Moreover, innovations in digital health and diagnostics contribute to the sector’s expansion.

Establish Your Business in India
Setting up Business in India
Distribution Channels
1. Online Platforms
Online platforms have gained significant popularity in India, offering a convenient way for businesses to reach a wide customer base. Over the three years, India has witnessed a surge in online shoppers reaching a staggering 127 million. Furthermore, it is projected that an additional 85 million individuals will join this trend by 2026. Brands can leverage platforms such as Amazon, Flipkart, and Myntra to tap into this growing segment and reach urban and semi-urban consumers.
2. Retail Partnerships
Collaborating with established retail partners such as Reliance Retail, DMart, and Croma can give access to vast networks and established customer bases. Companies can leverage their deep understanding of the market's established distribution channels and strong customer relationships. These partnerships also open up opportunities for in-store promotions, attractive product displays, and engaging activities that enhance the shopping experience for consumers. In addition, the international retail landscape in India has been rapidly expanding, with an influx of global brands, leveraging diverse entry strategies. Key companies in India like Aditya Birla Fashion and Retail Limited or Reliance Brands Limited are partnering with well-known international brands such as Armani, Hugo Boss, and Reebok. This reflects India’s growing e-commerce capabilities and rising consumer demand that encourages global brands to expand their footprint.
3. Direct Sales
Direct selling offers a unique opportunity for brands to build strong consumer relations and gain complete control over the distribution process and customer interactions. India’s direct sales sector saw revenue growth of 5.5% in the 2021-22 fiscal year, underscoring the importance of customer engagement through direct interactions.

How To Do Business in India
Starting a business in India offers immense opportunities for new entrants and businesses require a systematic approach to set up operations along with a foolproof market expansion strategy. For this, businesses need to understand market diversions and niches as well as consumer preferences. Foreign companies planning to expand their presence in India need a well-defined go-to-market strategy that aligns with the country’s market dynamics, regulatory landscape, and cultural diversity.
India Market Entry Strategies & Business Models
India has positioned itself as an attractive business destination with a vibrant economy skilled workforce, and a strategic geographical location, granting access to global trade routes. The country was ranked 63rd globally by the World Bank Report in 2020, significantly increasing from 142nd position in 2014.

Though the World Bank has paused these rankings, India’s business-friendly policies such as GST, digital initiatives, and bankruptcy reforms have resulted in rising foreign investments. Post-COVID recovery, several foreign companies looking to enter India are focused on market entry, aligning with their goals, local preferences, and regulatory requirements. Entering the Indian market requires a comprehensive strategy taking into consideration the stringent regulatory norms, constantly evolving economic landscape, and diverse consumer base. Here are some of the go-to-market entry strategies that businesses should consider:
Franchising Model
Franchising is a type of business model where an established company (the franchisor) gives another company (the franchisee) the right to use its brand, products, and business system. In return, the franchisee pays a fee and ongoing royalties. The franchise industry in India has been steadily growing, with both established brands expanding their presence and new franchise concepts emerging. Currently, the Indian franchise business is valued at around $ 47-48 billion and is growing at a rate of 30-36% per year. This industry employs over 1.6 million people and contributes nearly 5% to India’s GDP.
Wholly Owned Subsidiary
This type of entity enables a parent company to enter the Indian market and conduct business without having to establish a branch office. This arrangement allows the foreign parent company to leverage the legal system and economy while maintaining control over its subsidiary. It falls under the category of direct investment and is commonly referred to as Greenfield Investment. The establishment of a wholly owned subsidiary is regulated by the Companies Act 2013, and its associated rules. In recent times, India has simplified the process of incorporating a business by reducing fees and streamlining procedures. Moreover, with digitization all necessary documents can be easily accessed online making the incorporation process more efficient. The Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) in India permits up to 100% investment in sectors like manufacturing, e-commerce, and IT through approval. In some cases, complete control over business operations rests with the foreign entity.
Joint Venture
Joint ventures provide foreign entities with an opportunity to understand the Indian market establish local connections and access resources and capabilities that may not be easily attainable, through fully owned subsidiaries. In a JV a foreign company collaborates with an Indian partner, already engaged in business within the same field or area.
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
A Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is a business entity that combines the features of a limited liability company and a partnership firm. According to the regulations set by FEMA foreign investment up to 100% is permitted in LLPs operating in sectors that allow automatic route investments. LLPs are established at the level and registered under the Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008. One of the advantages of an LLP is its ease of management as it entails regulatory and compliance requirements.
Branch Office
Foreign companies are allowed to set up branch offices in India to conduct business. These branch offices can perform all activities of the foreign parent company, except for retail trading, manufacturing, and processing activities. If the foreign parent company wishes to engage in manufacturing services it must outsource these services through subcontracting. However, if the foreign company has made a profit in the preceding five years in its home country or has a net worth of at least $100,000 it needs to seek prior approval from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) before establishing a branch office.
Liaison Office
A liaison office acts as a communication hub between the foreign company and the Indian government enabling them to explore the feasibility of establishing a business in the country. However, a liaison office does not have the authority to enter into any agreements or contracts on behalf of its parent entity, nor does it have the authority for doing business in India. It is only responsible for collecting information and providing it to the parent company.
Legal & Regulatory Compliance
Starting a business in India involves adhering to legal and regulatory obligations. This entails acquiring licenses and permits registering the business with the relevant authorities and ensuring compliance, with labor laws and tax regulations.
Company Registration
When starting a business in India, it is crucial to complete the registration process with the appropriate authorities. In India, the prevalent forms of companies are private limited companies, public limited companies, and limited liability partnerships (LLPs). As of January 2023, more than 1. 50 million companies were registered in India.
Licenses and Permits
In India, setting up a business requires specific licenses and permits based on the type, size, and industry of the business. It could include a trade license, business registration certificate, and environmental clearance certificate such as Udyog Aadhar Registration, The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), the Import Export Code (IEC), and the Shop and Establishment Act License. It is crucial to research and obtain all the required licenses and permits before commencing operations.
Business Registration
In India, all businesses must undergo specific registration procedures to comply with national regulations. This involves registering with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs acquiring a Permanent Account Number (PAN) and Tax Deduction Account Number (TAN) from the Income Tax Department and enrolling for Goods and Services Tax (GST) and GSTIN registration. It is crucial to ensure that all the required registrations are duly completed before commencing operations.
Labor Laws and Tax Regulations
In India, businesses need to adhere to a variety of labor laws and tax regulations. This entails providing benefits like health insurance, and paid leave, as well as paying taxes on profits. It is crucial to research and comprehend these regulations before commencing operations. Some of the laws include the Factories Act of 1948, the Contract Labor Act of 1970, and the Building and Other Constructions Workers Act of 1996.
FDI & Investments
India has become a destination for foreign direct investors due to its economic reforms, strong economic growth, and young educated population and currently holds the 68th position in the Global Competitive Index. In the fiscal year 2021-22, India experienced a record level of FDI inflows amounting to $ 83.57 billion.
Sectors like information technology, telecommunications, and automobiles were the beneficiaries of FDI during this period. Furthermore, the government has introduced schemes and policies to promote development. One such example is the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme launched in 2020 for electronics manufacturing which aims to attract foreign investments. These initiatives offer incentives such as taxes, relaxed regulations, and easy access to land resources for investors looking to establish their businesses in India. As a result, there has been an increase, in job opportunities and overall economic growth.

How to Scale a Business in India
Scaling a business in India requires a holistic approach catering to the vast diversity of the country and diverse markets. Businesses need an agile approach to meet the changing demands of consumers by developing an omnichannel scale strategy and investing in local partnerships and alliances.
India B2B Go-to-Market Strategy
To enter the B2B go-to-market in India, companies need to understand the dynamics of the business landscape, diverse market trends, and changing consumer patterns. B2B businesses can effectively establish and expand their business in India due to its booming IT services, pharmaceuticals, automotive, and e-commerce.
Investment opportunities in India
India offers ample investment opportunities across various sectors considering the large consumer base, rapidly expanding economy, and government initiatives supporting domestic and foreign investments.
Infrastructure Investment in India: The Current Situation and Plans for the Future
India has been prioritizing infrastructure investments as a part of its economic growth strategy for years now. The government has launched several key initiatives for sectors such as transportation, energy, and digital infrastructure.
Roadways
India has one of the world’s largest road networks, covering around 6.3 million kilometers. The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) is responsible for the development, maintenance, and management of national highways. Major initiatives include Bharatmala Pariyojana, which aims to enhance and expand 34,800 kilometers of highways throughout the country.
Railways
India has the fourth-largest railway network globally, with over 13ooo km of track as of 2023. Divided into 18 zones ranks, the Indian Railways provides extensive passenger and freight services. The government is actively investing in modernizing and expanding railway infrastructure through high-speed trains and dedicated freight corridors. The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) for instance, aims to create a high-speed freight corridor connecting the capital region with Mumbai.
Airports
India currently has 138 operational airports and government plans to double the number to 300 by 2047 to cater to the growing demand. The government has also launched a regional connectivity scheme, Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik (UDAN) to improve regional connectivity and make air travel pocket-friendly. Major greenfield projects such as the Navi Mumbai International Airport and the Jewar Airport in Greater Noida, are transforming air travel. These airports can handle large volumes and provide direct connectivity to major urban centers.
Energy
India ranks 3rd in electricity production and consumption worldwide and has an installed power capacity of 442.85 GW as of April 2024. The country relies on a range of energy sources such as coal, natural gas, hydroelectric power, nuclear power, and renewable energy sources. The electricity generation from renewable and non-renewable sources for FY21 was 1,373.08 BU, 1,484.36 BU in FY22, and 1,617.72 BU in FY23. The renewable energy sector in India received USD 6.1 billion in FDI equity from April 2020 to September 2023 and around USD 3.8 billion in FDI in the solar energy sector over the past three fiscal years.
.webp)
The government has prioritized sustainability through initiatives such as the Ultra Mega Power Plants (UMPPs) and the National Solar Mission. These are aimed at increasing the proportion of renewable energy, within the overall energy mix.
Mobile Networks and Internet Connectivity
India has the world’s second-largest mobile phone users, with over 1. 2 billion subscribers and more than 624 million individuals accessing the internet as of 2023. To enhance mobile network access in underserved regions, the government launched the BharatNet initiative to provide high-speed connectivity to rural areas. This program aligns with the government's Digital India initiative that aims to reduce the digital gap by making internet access affordable and accessible to all citizens. 5G networks are currently being tested in certain urban areas.
Government Initiatives for Infrastructure Development
- Bharatmala Project: A national highways development project to improve road connectivity across the country.
- Objective: Enhanced transportation network, reduced logistics costs, improved trade and commerce.
- Sagarmala Project: A port-led development initiative to modernize ports and develop coastal economic zones.
- Objective: Boost in maritime trade, improved connectivity, increased employment opportunities.
- Digital India: A program to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy.
- Objective: Improved digital infrastructure, increased access to technology, enhanced e-governance services
- Smart Cities Mission: An urban renewal program to develop 100 smart cities with sustainable and efficient infrastructure.
- Objective: Enhanced quality of life, improved urban services, increased investment opportunities
- Make in India: The Make in India initiative launched by the government seeks to encourage both foreign companies to manufacture their products within the country. To bolster the manufacturing sector, generate job opportunities and foster economic growth this campaign has resulted in a doubling of foreign direct investment (FDI) to reach $ 83 billion as of 2021. Launched in September 2014, the Make in India campaign envisions transforming India into a manufacturing hub. It focuses on sectors such as automobiles, textiles, chemicals, electronics, and renewable energy. The Make in India has had a significant impact on the economy, attracting both foreign direct investment and facilitating the establishment of manufacturing units. FDI inflows peaked at $45.15 billion in 2014-15 and have been consistently high for eight consecutive years. The FDI peak in 2021-22 reached $84.8 billion. This substantial investment has originated from 101 countries across sectors spanning 31 Union Territories and States. Due to economic reforms and improvements, in Ease of Doing Business measures India is well-positioned to attract $100 billion worth of FDI during the current fiscal year.
.webp)
Raw Material Accessibility
Raw Material Availability in India
India possesses a wealth of natural resources and boasts a wide array of raw materials that cater to diverse industries. The nation's geographic positioning and geological characteristics play a vital role in its ample reserves of minerals, metals, and agricultural commodities. Some noteworthy raw materials found in India encompass iron ore, coal, bauxite, copper, and wheat.
Significance in Various Industries
The availability of raw materials in India has a significant impact on various industries, including:
1. Automotive Industry
The Indian automotive industry has witnessed significant growth due to the readily available raw materials such as steel, aluminum, and rubber in the country. According to the Ministry of Steel, India’s steel production grew at a CAGR of 4.3% from 2017-18 to 2021-22, reaching 122 million metric tons. Moreover, with 770000 metric tons of natural rubber produced in the fiscal year 2022, the automotive sector benefits from local supply to reduce costs and enhance production speed. For instance, Tata Motors, the world’s leading automotive company announced the expansions in response to increased demand.
2. Textile Industry
India’s textile industry is another beneficiary of raw materials, particularly cotton. India is renowned for its cotton production, which positions it as a significant participant in the global textile industry. Around 68% of India’s cotton comes from rain-fed regions while 35% originates from irrigated areas. In terms of productivity, India ranks 38th globally with a yield of 510 kg/ha. The availability of cotton has enticed both domestic and international textile companies to establish manufacturing facilities, in India.
3. Steel Industry
India is the second-largest producer of crude steel in the world with 35 billion tons of coking coal reserves and substantial iron ore deposits. This availability of raw materials has attracted investments from both domestic and international steel companies leading to substantial growth in India’s steel sector. Renowned companies like Tata Steel and JSW Steel have expanded their production capacities to keep up with this growth. Furthermore, the presence of these materials has not only benefited the steel industry but has also supported the development of related sectors such as construction and infrastructure.
Government Initiatives for Raw Material Availability
The Indian government has implemented several strategic policies to facilitate and encourage the availability of raw materials, within the country. These initiatives have had a significant impact on various industries and the overall economy.
- National Mineral Policy: Revised in 2019, this policy aims to ensure sustainable mining and mineral development. It promotes exploration, efficient extraction, and value addition of minerals.
- National Steel Policy: Released in 2017, this policy aims to increase domestic steel production and consumption. It focuses on raw material security, technology adoption, and sustainable growth.
- National Biofuel Policy: : Launched in 2018, this policy aims to promote the production and use of biofuels in India. It focuses on raw material availability, research and development, and market creation.
India's Offering to Your established Business
How India's Promising Benefits Can Fuel Growth in Your Established Businesses
India’s attractive benefits are fueling the growth of established foreign businesses. With an expanding economy, a large customer base, and a skilled workforce India presents a multitude of opportunities for foreign companies to expand their operations and increase their market share. According to the Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU), India has improved its quarterly forecast for the most favorable business environments in the next five years. In the EIUs published Business Environment Ranking (BER) on April 13th, this country has climbed six positions globally and moved from the 14th spot to the 10th, among 17 economies in Asia.
Numerous international companies have invested in manufacturing units within India as part of the Make in India initiative. The Make in India campaign has now completed eight years resulting in a foreign direct investment (FDI) doubling to $ 83 billion. Some notable examples include Samsung, Xiaomi, Hyundai, and Micron. These companies have expanded their manufacturing presence in India to capitalize on its growing consumer market and leverage government initiatives, aimed at promoting local manufacturing and production.
Xiaomi: India has recently revealed the establishment of another manufacturing plant, which brings the number of their manufacturing facilities to seven. As part of the Make in India initiative they have collaborated with Flex, an electronics manufacturing company to set up a facility spanning 1 million square feet in Chennai.
Micron: Micron, a computer storage chip manufacturer based in the United States recently revealed its plans to establish a semiconductor facility of $2.75 billion in Sanand near Ahmedabad. This announcement makes Gujarat the pioneer state, in India to house such a semiconductor manufacturing facility.
Subsidies and Benefits
The Indian government has implemented various initiatives to support the growth and diversification of established businesses. These initiatives provide benefits such as tax exemptions, grants, and other attractive incentives. Moreover, the government actively encourages businesses to invest in India by offering advantages such as access to untapped markets, affordable labor, and various resources, across different sectors including;
Textile Sector
The Indian government has given its approval to the production-linked incentive (PLI) schemes for the textile sector to boost manufacturing and exports of manmade fibers (MMF) garments and technical textiles. Over 5 years, this scheme is expected to offer incentives of Rs 10683 crore to support the production of these goods. The implementation of the PLI scheme is expected to attract investment in this particular industry segment.
Production-Linked Incentive Scheme
To promote domestic manufacturing and reduce the reliance on imports the Indian government introduced a scheme called PLI in March 2020. This scheme aims to provide incentives to companies based on their increased sales from products manufactured within the country. India’s PLI Scheme for Textiles has selected 64 textile investors, eligible to receive incentives over five years. Notably seven foreign companies from countries such, as the U.S., Japan, South Korea, Israel, Germany, and Sri Lanka have successfully applied through their subsidiaries.
- Gujarat is leading with the number of proposed projects while Madhya Pradesh has attracted the largest proposed investment.
- Apart from attracting foreign companies to establish operations in India, the initiative also seeks to promote the growth of domestic enterprises by establishing new manufacturing facilities or expanding existing ones.
- The Scheme has also received approval for sectors such as automobiles, pharmaceuticals, IT hardware such, as laptops, mobile phones, and telecom equipment, white goods, chemical cells, food processing, and more.
Battery Subsidy: The Indian government is in the process of developing a substantial subsidy program for companies involved in producing electricity grid batteries. This initiative is part of their commitment to transitioning towards energy. As per a proposal, from the power ministry, the draft scheme aims to provide a production-linked incentive subsidy of 216 billion rupees ($2.63 billion) over the decade from this year until 2030. The primary objective is to encourage companies to establish battery cell manufacturing facilities within India. The Financial Times has shared these details in their report.
Pharmaceuticals Sector:
India’s pharmaceutical industry is globally prominent, ranking third by volume at $50 billion. India contributes 3.5% to the export of drugs and medicines supplying them to, over 200 countries worldwide. To strengthen the industry’s resilience against shocks, ensure drug security, and promote domestic production of essential bulk drugs and high-value products, the Department of Pharmaceuticals has introduced three supportive schemes, The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme, Production Linked Incentive Scheme for Pharmaceuticals (PLI 2.0), and Scheme for Bulk Drug Parks. These schemes aim to encourage international players to invest more in these specific categories and increase their production capacity.

Semiconductor and Technology Sector
India’s technology sector, especially semiconductors, has gained prominence through initiatives aimed at developing a robust semiconductor system. The SemiconIndia 2023 event, launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, highlighted India’s commitment to building self-reliant manufacturing infrastructure. The government has allocated approximately $10 billion to subsidize semiconductor production. This subsidy is designed to attract global tech players, offering 50% support for setting up facilities in India, which can lead to $30 billion in total investments.
Social Security Agreements
India has entered into various agreements known as Social Security Agreements (SSAs) to simplify the social security responsibilities of workers who cross borders or work internationally. These agreements provide incentives such as the ability to work temporarily in another country, the transferability of pension benefits the combination of benefits from multiple countries, and the ability to withdraw social security benefits. As of 2023, India has signed SSAs with 20 countries, including Belgium, Germany, Switzerland, Denmark, Norway, Luxembourg, France, South Korea, Netherlands, and Hungary among others.

These SSAs offer three benefits for international workers and nonresident Indians (NRIs); temporary work opportunities in other countries (detachment), the ability to transfer pension benefits between countries (exportability), and the possibility of combining social security benefits from different countries (totalization).
- Workers who are detached from their home country and continue to contribute to their home country’s social security system as per the regulations of each Social Security Administration (SSA) can be exempted from making social security contributions in the host country for a period. To avail of this exemption employees must provide a 'Certificate of Coverage' (CoC) issued by their home social security authorities to the authorities in the host country.
- Exportability allows workers to receive social security benefits either in their home country or in the host country without any difference in the value of these benefits. This means that workers can transfer their benefits from the host country back to their home country or designate beneficiaries after retirement or when they complete employment there.
- Totalization considers the duration of an employee's work in a country when determining eligibility, for social security benefits. The payment amount is calculated based on how long the employee has worked in the foreign country.
Extensive Double Tax Avoidance Agreements
India has one of the most extensive networks of tax treaties aimed at avoiding double taxation and combating tax evasion. The country has established Tax Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs) with more than 85 other nations. The primary objective of these tax treaties is to establish a just system for determining which country has the right to tax different types of income based on whether it originates from the 'source' or 'residence' country. Through DTAAs taxpayers are safeguarded against being taxed and any hindrances to the smooth flow of international trade, investment, and technology transfer between two nations are prevented. Companies operating in countries that have a DTAA with India can benefit from more favorable provisions and rates available, under both the IT Act and the respective DTAA.
Incentives, Subsidies, & Government Plans for Setting up a Business in India
Developing a go-to-market strategy for startups in India requires an in-depth understanding of the rapidly digitizing economy and vast cultural diversity in the country. Startups need to focus on market segmentation and identify the diverse consumer demand. Government plays a crucial role in nurturing the advancement and progress of businesses in India. The government offers a range of subsidies, advantages, and incentives to stimulate entrepreneurship and investment, within the nation. These endeavors strive to forge a business atmosphere, foster economic expansion, and entice both local and foreign investors.
Subsidies and Grants for Startups
Funding Programs
The Indian government offers various funding programs to support startups. These programs provide financial assistance to startups at different stages of their growth. Some popular funding programs include:
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS):
- Provides financial support to startups in the ideation and development stages.
- Venture Capital Assistance (VCA) Scheme:
- Offers financial assistance to startups for the implementation of innovative projects.
- Credit Guarantee Fund Scheme for Startups (CGFS):
- Provides credit guarantee to startups for loans taken from financial institutions.
Incubators
The Indian government has established incubators to nurture and support startups. These incubators provide infrastructure, mentorship, and networking opportunities to startups. Some well-known incubators include:
- Atal Incubation Centers (AICs):
- Established under the Atal Innovation Mission to support startups in various sectors.
- Technology Business Incubators (TBIs):
- Promote innovation and entrepreneurship in technology-based startups.
- BioIncubators
- Support startups in the biotechnology sector by providing infrastructure and technical assistance.
Mentorship Initiatives
The Indian government has implemented mentorship initiatives to guide and support startups. These initiatives connect startups with experienced mentors who provide guidance and advice. Some notable mentorship initiatives include:
- Mentor India:
- A national mentorship initiative to support startups and entrepreneurs.
- NIDHI-EIR:
- Provides mentorship and financial assistance to startups through incubators.
- AIM-iCREST:
- Offers mentorship and support to startups in the field of robotics and AI.
These subsidies, grants, and initiatives aim to foster innovation and entrepreneurship in India by providing startups with the necessary support and resources to succeed.
Tax Benefits and Exemptions
1. Corporate Tax Rates
India offers competitive corporate tax rates, which can help alleviate the overall tax burden. Domestic companies are taxed at 30%, while foreign companies have a 40% rate. In 2019, the government lowered these rates to enhance economic growth, with eligible new manufacturing firms offering a reduced tax rate of 15%. This tax structure is favorable compared to the rates in China and the U.S.

2. Tax Holidays
The Indian government offers tax holidays to certain industries and businesses in order to stimulate investment and foster economic development. These tax holidays typically last for a period of 5 to 10 years during which eligible businesses are exempted from paying income tax. This can substantially alleviate the tax responsibilities for startups and also serve as an incentive for foreign investors to establish their businesses in India.
3. Special Economic Zones (SEZs)
India has set up Special Economic Zones (SEZs) to attract foreign investment and boost exports. Enterprises that operate within these SEZs enjoy a range of tax benefits and exemptions including being relieved from customs excise duties, central excise duties, and service tax. The SEZ policy came into existence in April 2000 to support economic growth along with attractive incentives at central and state levels. Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Telangana, Kerala, and Haryana are key states with most operational SEZs.

Companies based in SEZs are entitled to a reduced corporate tax rate of 15% for five years gradually increasing thereafter. These specialized zones provide an environment for businesses to thrive and significantly enhance their competitiveness, in the global market. As of 2024, more than 280 SEZs are operating in India, creating business opportunities for global and local players alike.
Labor and Wages Scenario in India
Availability of Skilled Labor and the Structure of Wages in India
Labor Market Overview
India possesses a varied workforce consisting of a population of more than 1.40 billion individuals. The rate of people actively participating in the labor force is relatively elevated showcasing several individuals actively seeking employment opportunities. Unemployment rates within India fluctuate among regions and sectors. On the whole, the nation has encountered levels of unemployment, particularly among young people and in rural areas. Government initiatives and skill development programs are being implemented to tackle this concern, with dedication and resolve.
Minimum Wage
The minimum wage in India differs depending on the state and industry. Its purpose is to guarantee that workers are fairly paid for their work. India offers the most competitive labor costs in Asia with a national minimum daily wage of around INR 176 (US$2.16) which amounts to approximately INR 5340 (US$65) per month.
Average Wages in Different Industries
The average wages in different industries in India can vary significantly. In India, men earn a salary of INR 1953000 while women earn an average salary of INR 1516200. Industries such as IT, finance, and healthcare tend to offer salaries whereas sectors like agriculture and construction, often have lower average wages.
Factors Influencing Wage Levels
- Education and Skills: Higher levels of education and specialized skills can lead to higher wages.
- Demand and Supply: The demand for certain skills and the availability of workers with those skills can influence wage levels.
- Industry and Location: Different industries and regions may have different wage levels based on factors such as cost of living and industry demand.
Government Initiatives for Skilled Labor and Wage Structure
- Skill India: Launched in 2015, aims to provide skill training to over 400 million people by 2022. Offers various programs and courses to enhance employability and bridge the skill gap.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): A flagship scheme of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship. Provides skill training and certification to youth across the country, with a focus on industry-relevant skills.
- National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS): Encourages employers to engage apprentices and provides financial incentives to both employers and apprentices. Aims to enhance the skills and employability of the youth.
- Minimum Wages Act: Ensures that workers receive fair wages for their work. Sets minimum wage rates for various industries and occupations to protect workers from exploitation and ensure a decent standard of living.
- Pradhan Mantri Rojgar Protsahan Yojana (PMRPY): Incentivizes employers to hire new employees by reimbursing the employer's contribution to the Employee Provident Fund (EPF) and Employee Pension Scheme (EPS) for a certain period.
India's Relations With Major Economies And Global Influence
India's Relations with Foreign Countries and Its Trustworthiness as a Global Business Hub
India has a significant role to play in global affairs and has been actively engaged in fostering diplomatic ties with other nations. Leveraging its cultural heritage, robust economy, and strategic geographical position, India has established itself as a prominent player, on the world stage.
India's Trade and Investment Policies
Openness to Foreign Investment
India has made several changes to attract foreign investment, such as relaxing its FDI policies and reducing limitations on foreign ownership in different industries. This open approach towards foreign investment has opened up many possibilities for global companies to set up operations in India and contribute to its economic development.
Promotion of Trade and Economic Cooperation
India is actively working towards promoting trade and economic cooperation with nations. They have entered into bilateral and regional trade agreements, aimed at improving market access and reducing trade barriers. Furthermore, India has set up platforms and initiatives like the India ASEAN Free Trade Agreement and the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement to strengthen economic ties and facilitate smooth trade, between India and its trading partners.
Market Plan in India's Strategic Partnerships
India’s strategic partnerships with countries including the U.S., Russia, Japan, and Australia create a supportive environment for businesses entering Indian market. These alliances extend across several sectors such as technology, trade, and defense. The India market strategy framework leverages these international partnerships to foster trade and enhance foreign investments.
United States
India and the United States share a strategic partnership in defense, technology, and trade. Both nations work together on projects to enhance their bilateral relationship. As of 2020, the U.S. has approved defense sales worth more than $20 billion, to India.
Russia
India and Russia share an enduring strategic alliance, especially in the field of defense. This partnership is based on the Agreement on the Programme for Military-Technical Cooperation, signed by both nations. They work together on defense initiatives conduct military exercises and exchange technology.
Japan
India and Japan share a strategic partnership that centers around collaborating on economic initiatives transferring technology and advancing infrastructure. A significant catalyst, for their thriving trade relationship has been the 2011 CEPA trade agreement, which has contributed to their trade volume reaching a noteworthy $ 21.96 billion during the fiscal year of 2022-23.
Australia
India and Australia share an alliance encompassing collaboration in defense, trade, and education. In June 2020 the two nations upgraded their relationship to a strategic partnership and reached a significant agreement enabling reciprocal access to military bases, for logistical support.
India's Commitment to Global Security
Peacekeeping Missions
India has played a vital role, in United Nations peacekeeping missions by actively participating for a considerable period. Indian peacekeepers have been deployed in areas of conflict worldwide working diligently to uphold peace and ensure stability.
Counterterrorism Efforts
India has actively participated in counterterrorism initiatives collaborating closely with global partners in the fight against terrorism. With experience, as a victim of terrorism, India recognizes the significance of collective efforts to tackle this global menace.
Maintaining Regional Stability
India plays a crucial role in upholding regional stability in South Asia. It actively participates in diplomacy to address conflicts and foster peaceful relationships with its neighboring nations. The commitment of India towards stability is vital for promoting economic progress and growth, within the region.
Market Entry Barriers in India
Though entering the Indian market is highly attractive for businesses, it involves several notable barriers. Some of the key barriers include:
Stringent Regulatory Complexities
India has a complex regulatory landscape with several sector-specific regulations, especially for retail and healthcare. These processes can be time-consuming as companies and businesses need to navigate local, federal, and state regulations.
High Cost of Compliance and Taxation
Despite the implementation of GST, businesses still face challenges due to varying tax policies across the country. Thus, compliance with GST or corporate taxes can be resource-intensive for foreign companies that are unfamiliar with India’s tax structure.
India market Entry Challenges and Solutions of Setting up a Business
India is renowned for its time-consuming bureaucratic processes, which can pose significant hurdles for businesses aiming to establish their presence in the country. From acquiring permits and licenses to adhering to labor laws dealing with paperwork and administrative procedures can feel overwhelming. Additionally, India’s infrastructure encompassing its roads, ports, and airports presents challenges for businesses seeking to operate within its borders. Substandard infrastructure can lead to delays, heightened expenses, and logistical obstacles. Moreover, India’s rich diversity with its multitude of cultures and languages adds another layer of complexity, for businesses venturing into the country. It becomes crucial for them to understand and respect customs and practices to thrive in this diverse environment.
Solutions
- Engaging the services of a lawyer or consultant who has expertise in the business environment can be beneficial, in maneuvering through the intricate regulations and bureaucratic processes.
- Developing connections, with government officials and business associations can facilitate the registration process and mitigate the chances of encountering corruption.
- Considering avenues for financing like crowdfunding or seeking support from angel investors can be beneficial in overcoming the challenges of restricted access, to conventional funding sources.
Our India Entry Strategy Consulting Services include:
- Consumer and market planning
- Demand and supply analysis
- Local partners and vendor identification and analysis
- Government regulations analysis
- Rik management
- Exploration of growth opportunities
How We Assist Businesses in Analyzing Indian Market Trends and Meeting Their Goals
Our go-to-market strategy for international businesses entering the Indian market is specifically designed to assist in navigating the intricate and ever-changing market landscape of India. We offer an approach that encompasses market analysis, localization, and collaborations to ensure a smooth entry into the Indian market. Our consulting services are tailored to provide a market strategy framework for businesses entering the market. Our team of professionals possesses extensive knowledge about the Indian business landscape, enabling them to help businesses overcome any cultural or regulatory obstacles they may encounter. We provide a range of comprehensive services, including assistance with entry strategies and compliance with regulations.
Contact Us


