Whole Exome Sequencing Market Regional Analysis:
North American Market Insights
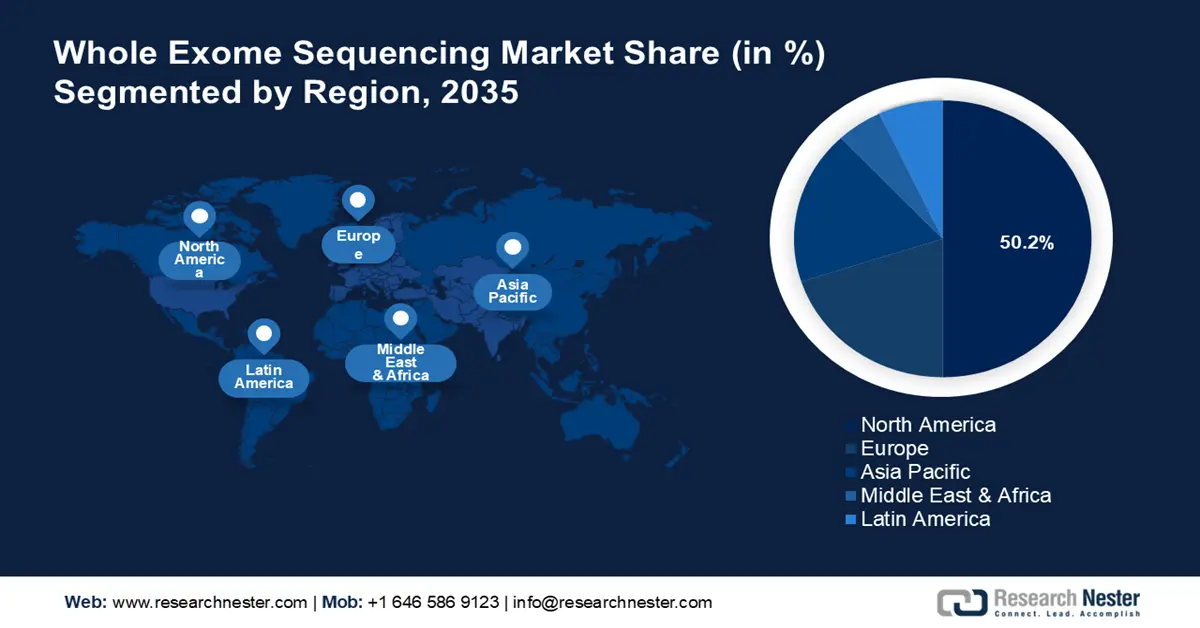
North America region is set to dominate around 50.2% market share by 2035, attributed to the rising prevalence of hereditary and chronic diseases and growing demand for targeted precision medicine. About half of all Americans (around 45%, or 133 million) experienced at least one chronic illness in 2018, and the number is rising. Chronic illnesses are a particular category of silent illness that, if not treated in a timely manner, could harm individuals irreversibly. Hence, the market for whole exome sequencing in North America is growing. Moreover, next-generation sequencing (NGS) is becoming a potent tool for delivering a deeper and more precise insight at the molecular underpinnings of individual tumors and specific receptors as genomics-focused pharmacology continues to play a greater role in the treatment of various chronic diseases, particularly cancer in North America.
Europe Market Insights
The European whole exome sequencing market is estimated to be the second largest, to have the highest growth over the forecast period. The Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and rising cancer rates have both had a big positive impact on the European market. The increased use of genetics in medicine has also significantly impacted the next-generation sequencing market in Europe's future expansion. Genome editing, gene synthesis, and next-generation sequencing are just a few of the technologies employed in genomics. Given the consistently falling cost of sequencing and strategic alliances between top corporations and premier research universities, the Germany market accounted for the greatest revenue share. A further factor in this region's market revenue increase is the rising prevalence of genetic diseases.
APAC Market Insights
Additionally, the whole exome sequencing market in Asia Pacific region is estimated to have the significant growth over the forecast period. The growth of the market in this region can be attributed to growing genetic abnormalities in this region. However, given the significant socioeconomic differences in the region and the paucity of research, knowledge, and health policies for those with rare diseases, managing rare diseases is particularly difficult in Asia and the Pacific. The area also struggles with a lack of medical knowledge and momentum when it comes to recognizing and meeting patients' unmet needs. Most crucially, these shortcomings are made worse by the paternalistic health systems in the area, where patients' opinions are rarely valued or heard. Hence, government are taking initiatives in order to spread awareness among people and also investing highly on research & development of exome sequencing.