Optical Satellite Communication Market Outlook:
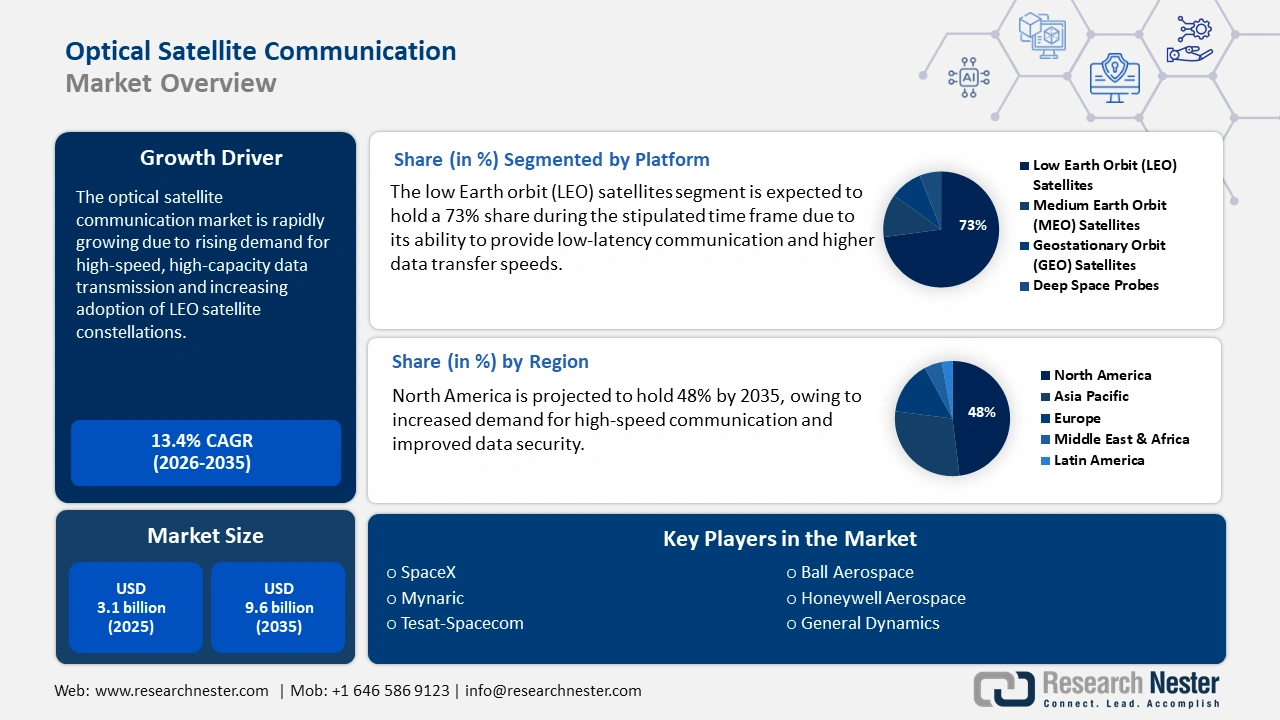
Optical Satellite Communication Market size was USD 3.1 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to reach USD 9.6 billion by the end of 2035, increasing at a CAGR of 13.4% during the forecast period, i.e., 2026-2035. In 2026, the industry size of optical satellite communication is estimated at USD 3.5 billion.
The worldwide optical satellite communication market is being thoroughly reshaped by different concurrent and powerful trends that are escalating its incorporation beyond usual projections. These include the vertical integration of OSC into LEO broadband constellations, standardization and commoditization, along with tactical partnerships and consolidation. According to an article published by the SHS in 2022, the latest high-resolution radar satellite, which is TerraSAR-X in Germany, as well as the U.S.-based Infrared experimental satellite NFIRE, effectively carried a two-way optical communication at a 5.625Gbit/s rate. This is considered a core operational demand for developing a space-driven internet backbone, which is suitable for the market’s growth.
Moreover, the demand for volume production, the sector’s transition from custom and one-off terminals to scalable, lower-cost, and modular designs, are also driving the market globally. In addition, strategies by the Europe-based Space Agency (ESA) under its Scylight program are proactively uplifting for standardization to reduce expenses and enhance interoperability. As per an article published by NLM in October 2022, a LEO spacecraft has the ability to ensure data transmission at an increased distance of an estimated 35,000 km. However, NASA’s Terabyte Infrared Delivery system (TBIRD) has successfully developed cubesat-suitable optical terminals, with a capability of 200 Gbps coherent LEO-to-ground downlink, thus suitable for the overall market.
Key Optical Satellite Communication Market Insights Summary:
Regional Insights:
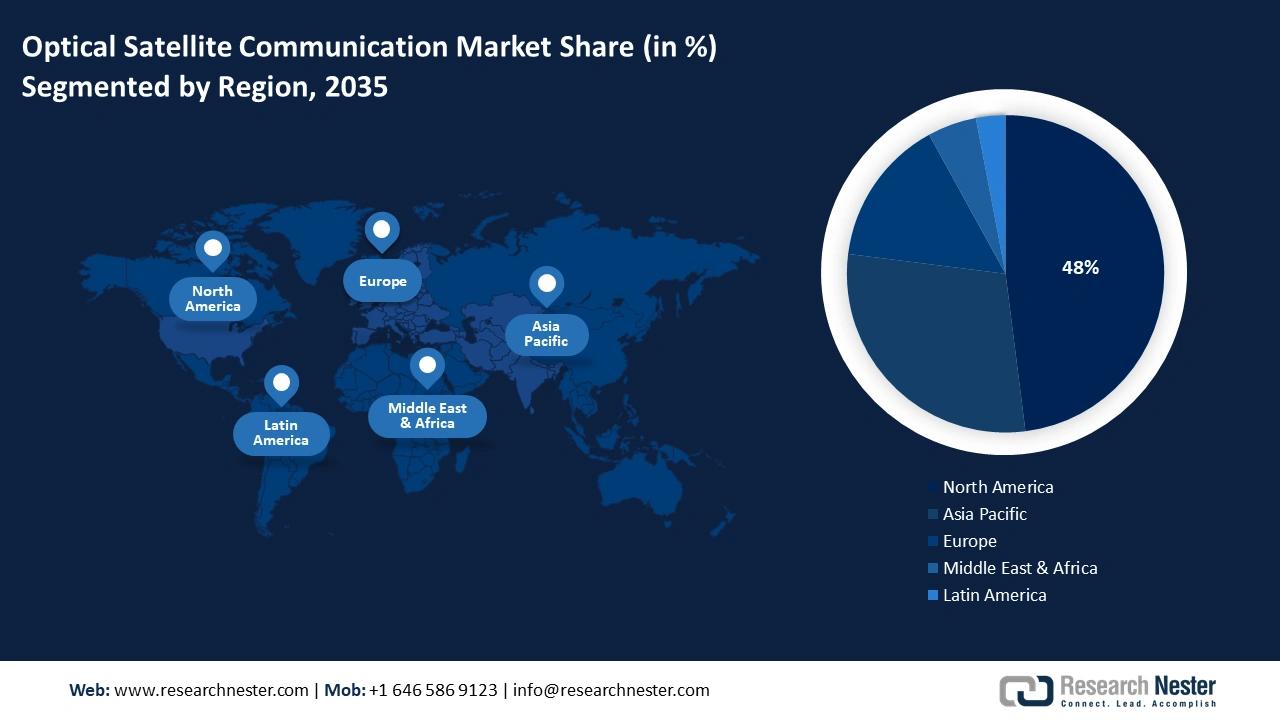
- North America in the Optical Satellite Communication Market is projected to hold the largest share of 48% by 2035, supported by technological innovation, vertical integration, and expanding commercial space capabilities.
- Europe is expected to witness the fastest growth through 2026–2035, owing to coordinated regional initiatives and substantial investments aimed at achieving tactical autonomy in secure space communications.
Segment Insights:
- The low earth orbit (LEO) satellites segment in the Optical Satellite Communication Market is projected to secure the highest share of 73% by 2035, propelled by the growing demand for low-latency, high-speed international communication and cost-effective, resilient connectivity solutions.
- The commercial segment is anticipated to capture the second-largest share by 2035, impelled by the large-scale deployment of LEO-based broadband megaconstellations such as SpaceX’s Starlink and Amazon’s Project Kuiper.
Key Growth Trends:
- Demand for secure and resilient communication
- Economic viability for data-based applications:
Major Challenges:
- Reliability and component performance in a harsh space environment
- Limitation in in-orbit demonstration and technology heritage
Key Players: SpaceX (U.S.),Mynaric (Germany),Tesat-Spacecom (Germany),Ball Aerospace (U.S.),Honeywell Aerospace (U.S.),General Dynamics (U.S.),Thales Alenia Space (France/Italy),Mitsubishi Electric (Japan),CACI International (U.S.),BridgeSat (U.S.),Astroptic (South Korea),SITAEL (Italy),Airbus Defence and Space (Europe),SSL (Maxar Technologies) (U.S.),ISRO (India),Space Engineering (Italy),AAC Clyde Space (UK/Sweden),Gilmour Space (Australia),BAE Systems (UK),NuSpace (Malaysia)
Global Optical Satellite Communication Market Forecast and Regional Outlook:
Market Size & Growth Projections:
- 2025 Market Size: USD 3.1 billion
- 2026 Market Size: USD 3.5 billion
- Projected Market Size: USD 9.6 billion by 2035
- Growth Forecasts: 13.4% CAGR (2026-2035)
Key Regional Dynamics:
- Largest Region: North America (48% Share by 2035)
- Fastest Growing Region: Europe
- Dominating Countries: United States, China, Germany, Japan, United Kingdom
- Emerging Countries: India, South Korea, Canada, France, Australia
Last updated on : 9 October, 2025
Optical Satellite Communication Market - Growth Drivers and Challenges
Growth Drivers
- Demand for secure and resilient communication: The need for this type of communication is extremely critical for the optical satellite communication market as it ensures data integrity, uninterrupted service, and confidentiality in the competitive and harsh space environment. According to an article published by the NLM in October 2024, the aspect of secured optical communication utilizes synchronized chaotic systems, and this particular solution is affordable, secure, and dependable with 1005 key consistency. In addition, this is also strong against any form of attacks, thereby making it effective for the market’s upliftment.
- Government-based R&D for next-generation capabilities: This driver is essential for the market, with the intention of developing next-generation capabilities in securing tactical national interests, driving advancements, and optical satellites. As per the May 2025 OECD data report, system failures continue to remain the actual cause of the communication network, constituting 93.5% of lost user hours in Europe as of 2022. In addition, malicious actions cater to 3.8% of lost user hours. Besides, as stated in the June 2025 PIB report, the Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF) in India has initiated a fund of more than ₹500 Crore (USD 56.3 million) to ensure R&D funding pertaining to telecom technologies, thus boosting the market’s exposure.
- Economic viability for data-based applications: These applications are crucial for the optical satellite communication market for transforming raw and high-volume imagery into suitable insights for different industries. For instance, as per the November 2024 NLM article, the Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO)-based Is-OWC system, as well as the Polarization Division Multiplexing (PDM), has been evaluated and readily operates at a 60 Gbps data rate. The system has achieved a 6.76 × 10⁻3 bit error rate at a 10,000 km transmission distance for channel 1 and 7.1 × 10⁻3 for channel 4, which positively caters to the market’s upliftment.
Optical Communication Approaches Driving the Optical Satellite Communication Market (2024)
|
Data Security Methods |
Benefits |
Remarks |
|
Simple optical chaos and dispersion compensation for transmitting data |
10 Gb/s gain over 100 km uss chaos and OptiSystem 7.0, along with a low bit error rate |
Limitation in distance transmission |
|
Chaotic encryption, pilot-specific signal processing, and physical layer security are inherently |
Encrypts 5 Gbaud 16QAM messages. Achieves BER ≤ FEC after 1600 km. Minimal distortion and high security. |
Complexity in digital-signal-induced chaos synchronization, and nonlinear effects, although minimal, are still present. |
|
Data encryption based on chaotic synchronization and hybrid entropy sources |
Achieves 200 km synchronization and passes overall NIST tests. Robust resilience and secured communication. Low-complex data encryption. |
Supports only 1.25 Gb/s data rate, and comprises hybrid system complexity. |
|
Chaotic signals as a secret key |
Achieves 100 Gb/s QPSK over 800 km. Enhances security with 40 Gb/s real-time encryption using FPGA. Effectively addresses transmission deficiencies. |
The complexity of deep learning and FPGA implementation, along with cost and expertise required |
|
Chaos synchronization with fiber channel characteristics to achieve high-speed, secure key distribution |
Achieves 100 Gbit/s key distribution with 100% key consistency. Long-term synchronization and secure according to NIST testing. Cost-effective and robust against attacks. |
Robustness against attacks is yet to be tested in all practical scenarios It may have unknown vulnerabilities Fewer practical scenarios |
Source: NLM
Challenges
- Reliability and component performance in a harsh space environment: Terminals in the market need to operate reliably for long-term years in harsh space environments, which comprise intense radiation, vacuum, and extreme temperature. These conditions can readily degrade severe components, which creates a negative impact on the market. Besides, laser diodes might experience decay in performance, due to which optics can be contaminated, and sensitive electronics can face damage, owing to radiation. Meanwhile, the aspect of ensuring a long-lasting operational lifetime without the need for maintenance requires extended radiation, continuous thermal management, and redundant systems, which causes a hindrance in the overall market.
- Limitation in in-orbit demonstration and technology heritage: Despite suitable demonstrations, the collective in-orbit operational hours for the aspect of technology in the optical satellite communication market are minuscule in comparison to historic heritage for RF systems. This deliberately lacks a long-lasting and statistically reliable record, making conservative stakeholders, especially defense and government, readily hesitant to bet on severe missions on optical satellite communication. Besides, insurers are also less familiar with failure modes, potentially resulting in increased premium expenses, thereby negatively impacting the market globally.
Optical Satellite Communication Market Size and Forecast:
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Year |
2026-2035 |
|
CAGR |
13.4% |
|
Base Year Market Size (2025) |
USD 3.1 billion |
|
Forecast Year Market Size (2035) |
USD 9.6 billion |
|
Regional Scope |
|
Optical Satellite Communication Market Segmentation:
Platform Segment Analysis
The low earth orbit (LEO) satellites segment in the market is anticipated to garner the highest share of 73% by the end of 2035. The segment’s exposure is effectively fueled by low-latency, high-speed international communication, high-resolution provision, and cost-effective, along with resilient solution provision for the digital division. For instance, according to an article published by Australia Government in September 2024, more than 10% of agricultural workers are dependent on LEO satellites. Additionally, 84.2% of agriculture-based businesses have internet connectivity, and by the end of 2022, almost 99.8% businesses in the industry will have broadband internet accessibility, thereby suitable for the segment’s exposure.
End user Segment Analysis
The commercial segment in the optical satellite communication market is predicted to account for the second-highest share during the forecast timeline. The segment’s upliftment is highly attributed to the robust deployment of commercial broadband megaconstellations in LEO, including SpaceX’s Starlink, along with planned systems from Amazon’s Project Kuiper. For these particular entities, optical satellite communication terminals are not only an enhancement but an ultimate infrastructure component, which has enabled high-speed ISL that develops a suitable space-based network, reducing dependency on ground stations. Besides, the burgeoning Earth Observation industry depends on OSC for increasing the downlinking of huge data volumes from hyperspectral and high-resolution satellites, thus suitable for boosting the segment.
Application Segment Analysis
The inter-satellite link (ISL) segment in the market is expected to cater to the third-highest share by the end of the projected period. The segment’s development is driven by its vitality for the upcoming production of satellite systems, since these can provide direct communication, optimize navigation accuracy, improve satellite network efficacy, and permit autonomous constellations by diminishing dependency on ground stations. As per the April 2025 NLM article, an increase in orbit determination accuracy is possible with ISL measurement data addition from 6 regional and 16 global stations in China. Owing to this, the accuracy has surged by 40% and 80%, thus bolstering the segment’s upliftment.
Our in-depth analysis of the global market includes the following segments:
|
Segment |
Subsegments |
|
Platform |
|
|
End user |
|
|
Application |
|
|
Range |
|
|
Data Rate |
|
|
Component |
|

Vishnu Nair
Head - Global Business DevelopmentCustomize this report to your requirements — connect with our consultant for personalized insights and options.
Optical Satellite Communication Market - Regional Analysis
North America Market Insights
North America in the optical satellite communication market is anticipated to account for the largest share of 48% by the end of 2035. The market’s exposure in the region is highly driven by technological demonstration and innovation, vertical integration, commercial market scale, tactical focus on suitable communications, and sovereign capabilities. In this regard, the October 2024 MITRE Organization data report denoted that the space economy in the U.S. has generated more than USD 211 billion and successfully employs 360,000 people in the overall region, thereby suitable for boosting the market.
The market in the U.S. is growing efficiently, owing to the presence of the Space Development Agency (SDA) and the U.S. Space Force, effectively developing a proliferated low-Earth orbit (pLEO) constellation. In addition, the aspect of commercial advancement and unparalleled defense expenditure is also driving the market in the country. As per a data report published by the Center for Space Policy and Strategy in June 2024, USD 29.6 billion has been requested for the regional Space Force, which is almost 3.5% of the Department of Defense’s overall budget request, which denotes an optimistic outlook for the overall market.
Canada market is also growing due to the provision of strategic governmental investment in niche capabilities, along with a robust commercial anchor in Telesat’s Lightspeed constellation. Besides, the Canada-based Space Agency (CSA) has readily focused on scientific contribution and technological sovereignty, as well as generously funding OSC R&D through standard programs, such as the Lunar Exploration Accelerator Program. According to an article published by the Space Insider in April 2024, there has been a surge in the fund provision for the Lunar Exploration Accelerator Program (LEAP), amounting to USD 8.6 million by the end of 2025, which is suitable for the market’s exposure in the country.
Frequency Considerations of Spacecraft in North America (2025)
|
Band |
Frequency |
|
HF |
3 to 30 MHz |
|
VHF |
30 to 300 MHz |
|
UHF |
300 to 1000 MHz |
|
L |
1 to 2 GHz |
|
S |
2 to 4 GHz |
|
C |
4 to 8 GHz |
|
X |
8 to 12 GHz |
|
Ku |
12 to 18 GHz |
Source: NASA Government
Europe Market Insights
Europe market is predicted to emerge as the fastest-growing region during the forecast timeline. The market’s development in the region is subject to the coordinated and substantial support for the market, with the objective of offering tactical autonomy in secure space communications. Besides, as stated in the February 2022 Europe Commission data report, an initiative has been undertaken for space-based secure connectivity by providing approximately €6 billion. This also includes the Union’s contribution, with a valuation of €2.4 billion as of 2022, thereby creating an optimistic outlook for the market in the region.
The optical satellite communication market in the UK is gaining increased traction, owing to the strategic and early commitment to sovereign space capabilities and a suitable regulatory environment. In addition, the UK Space Agency's National Space Strategy has prioritized leadership in satellite communications, which directly funds OSC R&D. Besides, according to an article published by the CSIS Organization in July 2025, the relationship between the U.S. and the UK has resulted in the development of country’s defense sector, with the Ministry of Defense investing USD 40 billion and readily supporting 440,000 job opportunity, which denotes a huge growth opportunity for the market.
The market in Germany is also developing due to the aspect of deep-seated expertise in precision photonics and engineering, along with unparalleled industrial manufacturing. In addition, the regional Aerospace Center readily makes the provision of a continuous stream of increased R&D, which successfully acts as a suitable technological incubator for the commercial sector. Besides, the market’s growth in the country is further propelled by its role in the regional defense initiatives, wherein secured and jam-resistant communications are considered top priorities.
APAC Market Insights
Asia Pacific in the optical satellite communication market is expected to grow steadily by the end of the predicted timeline. The market’s exposure in the overall region is highly attributed to the existence of national strategic ambitions, huge government investment, and burgeoning commercial space sectors, along with the aspect of advanced technological prowess. As per an article published by the Acta Astronautica in October 2025, 90% of the population in India currently receives space-driven television, in comparison to 20% in previous years, thereby denoting the importance of the market in the overall region.
China market is gaining increased traction, owing to the wide-ranging national strategy for space dominance, the multi-faceted program by the China National Space Administration (CNSA), government spending on space facilities, and the increasing demand for regional manufacturers. As stated in the January 2022 CNSA Government report, the country has immensely focused on developing different kinds of satellites and satellite technology, based on which telecommunication satellites and remote-sensing satellites account for almost 71% of the overall satellites deliberately introduced by the country.
The optical satellite communication market in India is also growing due to the contribution of the ISRO in making optical satellite communication the ultimate cornerstone of its upcoming architecture. According to an article published by the ISRO in 2022, the aspect of technology transfer, with the objective of developing space applications and space systems, utilization successfully made distributions of almost 30% in chemicals and materials sector, followed by 26% in telecom broadcasting navigation, 18% in electronics and computer-based systems, and 13% in both optical instruments as well as mechanical and electro-mechanical industries.
Key Optical Satellite Communication Market Players:
- SpaceX (U.S.)
- Company Overview
- Business Strategy
- Key Product Offerings
- Financial Performance
- Key Performance Indicators
- Risk Analysis
- Recent Development
- Regional Presence
- SWOT Analysis
- Mynaric (Germany)
- Tesat-Spacecom (Germany)
- Ball Aerospace (U.S.)
- Honeywell Aerospace (U.S.)
- General Dynamics (U.S.)
- Thales Alenia Space (France/Italy)
- Mitsubishi Electric (Japan)
- CACI International (U.S.)
- BridgeSat (U.S.)
- Astroptic (South Korea)
- SITAEL (Italy)
- Airbus Defence and Space (Europe)
- SSL (Maxar Technologies) (U.S.)
- ISRO (India)
- Space Engineering (Italy)
- AAC Clyde Space (UK/Sweden)
- Gilmour Space (Australia)
- BAE Systems (UK)
- NuSpace (Malaysia)
The international optical satellite communication market is effectively competitive and is readily characterized by a tactical divergence between specialized terminal manufacturers, such as Tesat and Mynaric, along with vertically integrated mega-constellation operators, including SpaceX. Besides, notable players are strongly adopting two essential strategies, which include the development of ultra-secure, defense, and high-performance systems for governmental contracts and affordable mass production to cater to the burgeoning commercial LEO market. Besides, suitable approaches are readily dominated by robust R&D investment to optimize data rates and ensure form-factor reduction by constituting the formation of tactical alliances to achieve design wins in the majority of constellation programs, thus making it suitable for the market globally.
Here is a list of key players operating in the market:
Recent Developments
- In January 2025, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, along with NEC Corporation readily performed the world’s first-ever rapid optical communication by utilizing LUCAS between the Optical Data Relay Satellite and the Advanced Land Observing Satellite-4 DAICHI-4.
- In December 2024, Airbus, along with the French Space Agency (CNES), declared the completion of the TELEO in-orbit demonstrator, which has been successfully designed to prove that huge and rapid ground is suitable to ensure data transfer.
- In June 2024, Safran Electronics & Defense successfully developed the latest solution for effectively transmitting and receiving optical communications through laser, which enabled armed forces to share information at a rapid speed
- Report ID: 3870
- Published Date: Oct 09, 2025
- Report Format: PDF, PPT
- Explore a preview of key market trends and insights
- Review sample data tables and segment breakdowns
- Experience the quality of our visual data representations
- Evaluate our report structure and research methodology
- Get a glimpse of competitive landscape analysis
- Understand how regional forecasts are presented
- Assess the depth of company profiling and benchmarking
- Preview how actionable insights can support your strategy
Explore real data and analysis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Free Sample includes current and historical market size, growth trends, regional charts & tables, company profiles, segment-wise forecasts, and more.
Connect with our Expert
Copyright @ 2026 Research Nester. All Rights Reserved.




