Open Source Vulnerability Scanner Market Outlook:
Open Source Vulnerability Scanner Market size was valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2025 and is set to exceed USD 4.07 billion by 2035, registering over 13% CAGR during the forecast period i.e., between 2026-2035. In the year 2026, the industry size of open source vulnerability scanner is estimated at USD 1.34 billion.
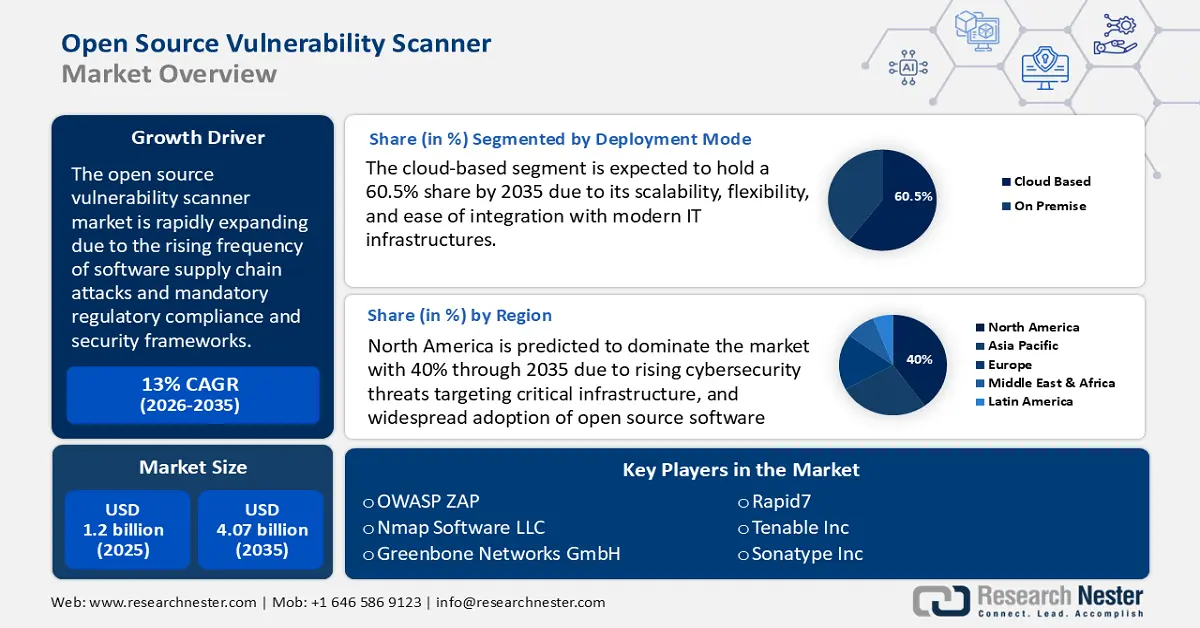
The market is primarily driven by the rising frequency of software supply chain attacks. The rise in software supply chain attacks is a primary catalyst for adopting open-source vulnerability scanners. These tools enable continuous monitoring of software components for known vulnerabilities, helping organizations protect against tampering and exploitation. These scanners are no longer niche tools but are strategic assets for modern organizations navigating a volatile cybersecurity landscape. As federal incentives, developer workflows, and digital transformation initiatives converge, the market is expected to witness sustained growth.
A recent and impactful example of a software supply chain attack is the 2023 MOVEit Transfer vulnerability, which was exploited by the Clop ransomware gang to breach data from hundreds of organizations worldwide, including U.S. federal agencies, banks, and universities. MOVEit, a managed file transfer software widely used by enterprises and government agencies, was compromised through a zero-day vulnerability. Attackers were able to inject malicious code into the software’s supply chain, which allowed them to exfiltrate sensitive data. In response, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency issued a public advisory and added the CVE to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog, directing organizations to mitigate the threat immediately. Additionally, organizations using open source scanners such as Trivy, Grype, or OpenVAS connected to the NIST vulnerability database were able to detect and fix the issue faster. This attack highlights the growing risk of supply chain threats and the crucial role open source scanners play in protecting software systems.
Key Open Source Vulnerability Scanner Market Insights Summary:
Regional Highlights:
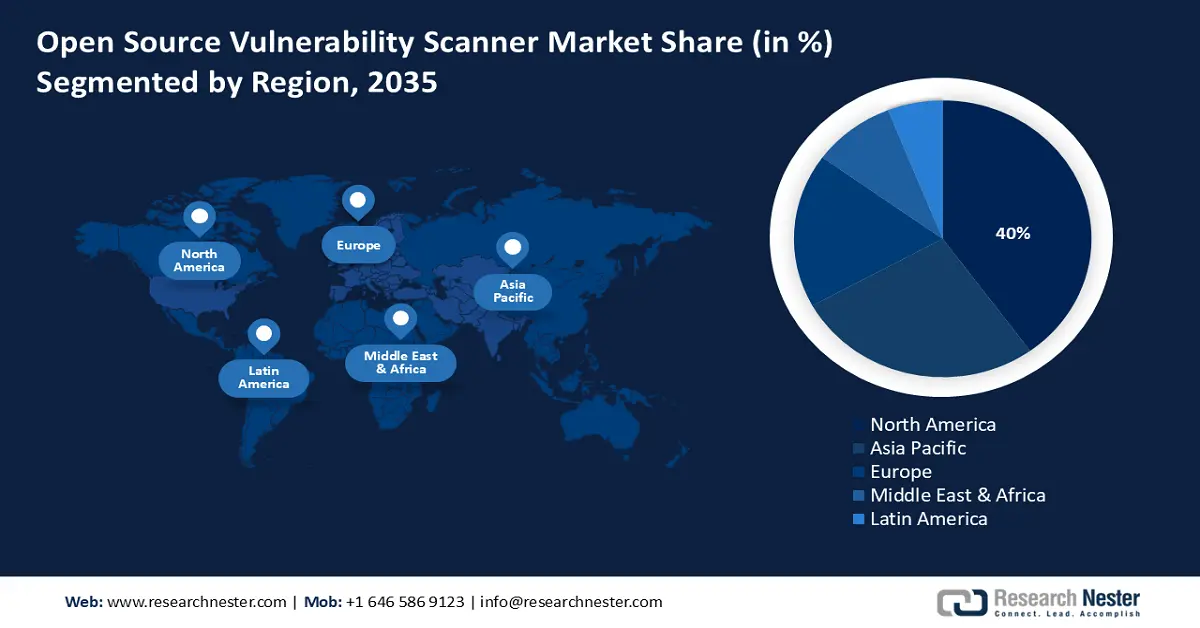
- North America is poised to secure over 40% revenue share by 2035 in the open source vulnerability scanner market, due to rising cybersecurity threats targeting critical infrastructure.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to command a significant share from 2026-2035, owing to cybersecurity threats and increased cybercrime losses.
Segment Insights:
- The cloud-based segment is projected to hold around 60.5% share by 2035 in the open source vulnerability scanner market, propelled by its scalability, flexibility, and ease of integration with modern IT infrastructures.
- By 2035, the web application vulnerability scanners segment is expected to capture over 65% share, fueled by the surge in web-based services and digital transformation across industries.
Key Growth Trends:
- Mandatory regulatory compliance and security frameworks
- Widespread adoption of DevSecOps
Major Challenges:
- Lack of enterprise level support and accountability
- Integration complexity and skill gaps
Key Players: OWASP ZAP, Nmap Software LLC, Greenbone Networks GmbH, Rapid7, W3af, Subgraph OS, Tenable, Inc., Atomicorp, Sonatype, Inc.
Global Open Source Vulnerability Scanner Market Forecast and Regional Outlook:
Market Size & Growth Projections:
- 2025 Market Size: USD 1.2 billion
- 2026 Market Size: USD 1.34 billion
- Projected Market Size: USD 4.07 billion by 2035
- Growth Forecasts: 13%
Key Regional Dynamics:
- Largest Region: North America (40% Share by 2035)
- Fastest Growing Region: Asia Pacific
- Dominating Countries: United States, China, Germany, United Kingdom, Japan
- Emerging Countries: India, South Korea, Brazil, Singapore, Australia
Last updated on : 3 December, 2025
Open Source Vulnerability Scanner Market - Growth Drivers and Challenges
Growth Drivers
- Mandatory regulatory compliance and security frameworks: Open source vulnerability scanners are instrumental in helping organizations meet the requirements of cybersecurity frameworks and regulations. For instance, under the Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA), U.S. Federal agencies are required to implement risk-based security programs. Tools such as OpenVAS and OSV-Scanner support these efforts by enabling regular vulnerability assessments in line with standards provided by NIST’s SP 800-53, which details recommended security controls. With global compliance laws demanding documented vulnerability management practices, these scanners offer a transparent and auditable solution.
- Widespread adoption of DevSecOps: The shift towards DevSecOps encourages embedding security early in the development cycle. Open source scanners such as OWASP Dependency Check and Clair are increasingly integrated into CI/CD pipelines, enabling developers to identify and resolve issues in real-time. This alignment with DevSecOps reduces time to market and supports continuous security monitoring.
- Public sector and non-profit push for open source adoption: Government and non-profit agencies are endorsing open source solutions to improve security transparency, reduce vendor lock-in, and stimulate ecosystem innovation. This support has elevated the trust and usage of open source scanners across sectors. Additionally, government-backed efforts such as CISA’s Zero Trust mandates and initiatives from the Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF) are fueling the credibility and adoption of open source security tools. For instance, in 2023, the Linux Foundation’s OpenSSF launched the Alpha-Omega Project, in collaboration with CISA and NIST, to fund critical security tools and improve scanning across widely used open source projects. This initiative empowered the use of scanners such as Syft and Grype, which detect software bills of materials (SBOMs) vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure applications. The initiative aims to prevent vulnerabilities from reaching production environments by enhancing scanner precision and integration.
Challenges
- Lack of enterprise-level support and accountability: While open source vulnerability scanners offer flexibility and cost-effectiveness, they often lack formal support structures such as service-level agreements, dedicated customer service, or guaranteed updates. This can be a concern for enterprises handling sensitive or regulated data, where downtime, delayed patches, or misconfigurations may carry serious operational and compliance risks.
- Integration complexity and skill gaps: Deploying and managing open source vulnerability scanners require cybersecurity and DecSecOps expertise, particularly for configuring integrations with CI/CD pipelines, container registries, or SBOM frameworks. Many organizations face a shortage of skilled professionals who can fine-tune these tools for optimal performance and accuracy.
Open Source Vulnerability Scanner Market Size and Forecast:
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Year |
2026-2035 |
|
CAGR |
13% |
|
Base Year Market Size (2025) |
USD 1.2 billion |
|
Forecast Year Market Size (2035) |
USD 4.07 billion |
|
Regional Scope |
|
Open Source Vulnerability Scanner Market Segmentation:
Deployment Mode Segment Analysis
Cloud-based segment is predicted to account for around 60.5% open source vulnerability scanner market share by 2035, due to its scalability, flexibility, and ease of integration with modern IT infrastructures. It allows real-time scanning across distributed environments, including hybrid and multi-cloud setups. This deployment mode supports automated updates and centralized management, making it ideal for dynamic DevSecOps workflows. Its lower infrastructure cost and faster deployment also appeal to SMEs and large enterprises.
Application Segment Analysis
By 2035, web application vulnerability scanners segment is expected to capture over 65% open source vulnerability scanner market share, due to the surge in web-based services and digital transformation across industries. These scanners detect critical flaws such as SQL injection, XSS, and broken authentication in real-time. As organizations adopt agile and DevSecOps practices, the demand for continuous web application testing becomes essential. Open sources tools such as OWASP ZAP are gaining popularity for their effectiveness, cost efficiency, and easy CI/CD integration.
Our in-depth analysis of the global market includes the following segments:
|
Deployment Mode |
|
|
Application |
|
|
End use |
|

Vishnu Nair
Head - Global Business DevelopmentCustomize this report to your requirements — connect with our consultant for personalized insights and options.
Open Source Vulnerability Scanner Market - Regional Analysis
North America Market Insights
By 2035, North America open source vulnerability scanner market is poised to capture over 40% revenue share, due to rising cybersecurity threats targeting critical infrastructure, and widespread adoption of open source software. Organizations are prioritizing cost-effective, transparent tools that align with evolving compliance mandates. The region’s robust developer community encourages innovation and rapid adoption. Additionally, government backed cybersecurity initiatives are boosting trust in in open source security solutions.
The U.S. market is growing as enterprises face increased risks from software supply chain attacks. These tools are essential for identifying hidden flaws in widely used open source components. Additionally, regulatory pressures such as SBOM (Software Bill of Materials) mandates, are driving adoption. In August 2024, the U.S. Army mandated the inclusion of SBOM’s in its software contracts to enhance cybersecurity. To comply, organizations have increasingly adopted open source vulnerability scanners for automated SBOM generation and management.
In Canada, the open source vulnerability scanner market is growing rapidly due to the government’s proactive cybersecurity initiatives. In February 2022, the Government in Canada is allocated USD 59 million to the National Cybersecurity Consortium to enhance research and development in this field. The rapid adoption of cloud technologies has increased the need for robust security measures, prompting organizations to invest in open source scanning tools for comprehensive protection. Additionally, collaborations between tech companies also enrich the cybersecurity ecosystem, fostering innovation and widespread adoption of these solutions.
Asia Pacific Market Insights
Asia Pacific is anticipated to garner a significant share from 2026 to 2035, owing to cybersecurity threats and increased cybercrime losses. Countries in the region are proactively enhancing their cybersecurity frameworks, exemplified by substantial investments to bolster national resilience against online threats. For instance, in February 2025, OpenText announced a significant expansion of its investments in the Asia Pacific, focusing on enhancing cloud, security, and AI infrastructure across countries including Japan, Singapore, Australia, Korea, and India. This strategic initiative includes the development of centers of excellence in research and development, professional services, and operations, with plans to increase by 2500 over the next three years. This proactive stance by OpenText is committed to expanding its cloud delivery capabilities to better serve its customers' needs in the region.
China’s open source vulnerability scanner market is experiencing significant growth driven by stringent government regulations mandating the reporting of software vulnerabilities within 48 hours, thereby necessitating robust scanning tools. The rapid digital transformation across industries has heightened the need for effective vulnerability management solutions to protect expanding digital infrastructures in China. Furthermore, the increasing complexity of cyber threats has prompted organizations to adopt advanced scanning technologies to safeguard sensitive data and maintain compliance with evolving security standards.
The open source vulnerability scanner market in South Korea is experiencing notable growth driven by the country’s rapid digital transformation and the increasing adoption of open source software across various industries. The integration of DevSecOps practices has further emphasized the need for robust vulnerability management tools to ensure secure software development lifecycles. Additionally, government-backed AI and 5G expansions are accelerating the need for scalable and automated security tools.
Open Source Vulnerability Scanner Market Players:
- OWASP ZAP
- Company Overview
- Business Strategy
- Key Product Offerings
- Financial Performance
- Key Performance Indicators
- Risk Analysis
- Recent Development
- Regional Presence
- SWOT Analysis
- Nmap Software LLC
- Greenbone Networks GmbH
- Rapid7
- W3af
- Subgraph OS
- Tenable, Inc.
- Atomicorp
- Sonatype, Inc
The leading companies in the open source vulnerability scanner market leverage proprietary enhancements on open frameworks for superior performance. Their ability to offer end-to-end security integration across CI/CD pipelines sets them apart. Additionally, trusted brand reputations and dedicated threat intelligence teams strengthen their market position. Here are some leading players in the market:
Recent Developments
- In March 2025, Google added major updates to its free open source vulnerability scanner OSV-Scanner, by including features from OSV-SCALIBR to help open source developers detect issues more effectively.
- In March 2025, CrowdStrike introduced new features in its CrowdStrike Falcon Exposure Management system. These updates improve the way companies handle cybersecurity by replacing old tools and using AI to prioritize risks. The system helps teams find and fix serious security issues in devices such as routers, switches, and firewalls in real time without needing extra scanners, agents, or hardware.
- In February 2025, Semgrep a company that creates tools to find security issues in software code, raised USD 100 million in funding, bringing its total to USD 204 million. The company is developing automated vulnerability detection services.
- Report ID: 7571
- Published Date: Dec 03, 2025
- Report Format: PDF, PPT
- Explore a preview of key market trends and insights
- Review sample data tables and segment breakdowns
- Experience the quality of our visual data representations
- Evaluate our report structure and research methodology
- Get a glimpse of competitive landscape analysis
- Understand how regional forecasts are presented
- Assess the depth of company profiling and benchmarking
- Preview how actionable insights can support your strategy
Explore real data and analysis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Free Sample includes current and historical market size, growth trends, regional charts & tables, company profiles, segment-wise forecasts, and more.
Connect with our Expert
Copyright @ 2026 Research Nester. All Rights Reserved.




