Nontuberculous Mycobacterium Treatment Market - Regional Analysis
North America Market Insights
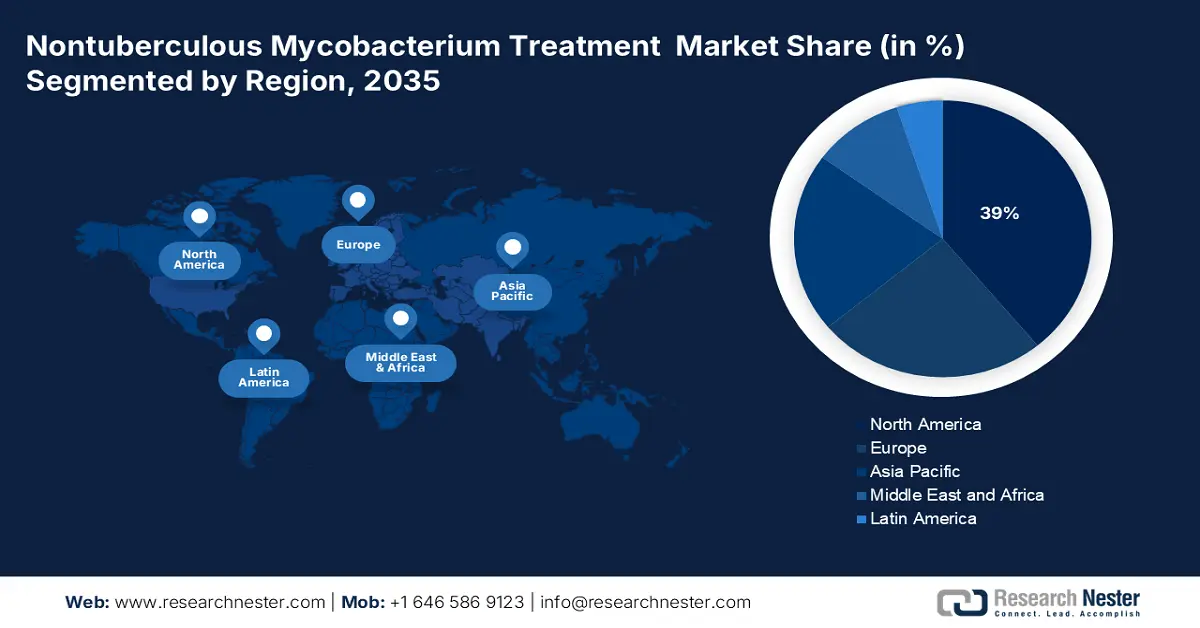
North America is anticipated to capture the highest share of 39% in the global nontuberculous mycobacterium treatment market by the end of 2035. The growth is fueled by a growing number of patients, an aging population, and better diagnostic methods. As per the report from Ontario in February 2024, Ontario increased investments of USD 110 million to benefit an additional 328,000 patients annually. Government initiatives are promoting early intervention and cost-effective treatment strategies, resulting in better patient outcomes and fewer hospitalizations. Further, rising public health awareness, enhanced diagnostic standards, and R&D for enhanced regimens also boost the market.
The nontuberculous mycobacterium treatment market in the U.S. is driven by an aging population experiencing chronic respiratory infection. Enhanced screening and diagnostic capabilities, supported by federal investment, rising detection rates of cases, and expanding treatment. The American Lung Association report of 2025 describes that 35.2 million individuals suffer from chronic lung disease in 2023, and the number of death cases enrolled through lung disease in 2022 was 586,000. This increasing disease burden emphasizes the urgent requirement for novel therapies and continued healthcare investment in the NTM treatment environment.
Prevalence of NTM disease in 2023
|
Country |
Prevalence |
|
U.S. |
3.1/100,000 to 4.7/100,000 |
|
Canada |
19.0 cases/100,000 persons |
Source: NLM September 2023, NLM July 2023,
APAC Market Insights
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the global nontuberculous mycobacterium treatment market throughout the discussed period. The expansion in this area is created by a combination of rising disease rates, the growth of healthcare infrastructure, and an increased emphasis by governments on infectious disease controls. Significant factors contributing to this growth include improvements in diagnosis, increased education of healthcare providers, and increased investment in drug development and access programs.
Over the last five years, the government in China has increased spending on NTM treatment. The national programs have built a pathway for access to treatment through healthcare changes and insurance policies. As more people live in cities and pollution and respiratory problems evolve into an epidemic, the number of NTM patients is expected to climb as well. As per the NLM report in May 2024 states that the prevalence of NTM cases in China was 6.4%. The large at-risk population due to COPD and aging contributes to significant market growth potential.
Europe Market Insights
The Europe nontuberculous mycobacterium treatment market is expected to display steady growth as a result of increased disease prevalence, an aging population. Healthcare systems across the region are increasing their budgets to meet the demands of the growing NTM treatment population. To meet this need, the European Commission is prioritizing health-based initiatives that focus on increasing NTM research and improving patient care pathways. There are other factors fueling market growth, including government reimbursement policies and an increasing knowledge base of clinicians regarding the complex treatment challenges associated with NTM infections. Current trends include personalized medicine and combination therapies to improve treatment outcomes.
Germany holds the largest share in the NTM treatment market within Europe in the forecast period. According to the NLM report in December 2023, the prevalence of NTM cases ranges between 5.3 to 5.8 per 100,000 population annually. The federal budget has expanded to include NTM-focused research and reimbursement programs, all of which help new drug therapies become accessible - positioning Germany as a growth center. The presence of many professional pharmaceutical companies focused on respiratory, infectious diseases, and combinations of both, is also an important facilitator for the market expansion.