Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Market Outlook:
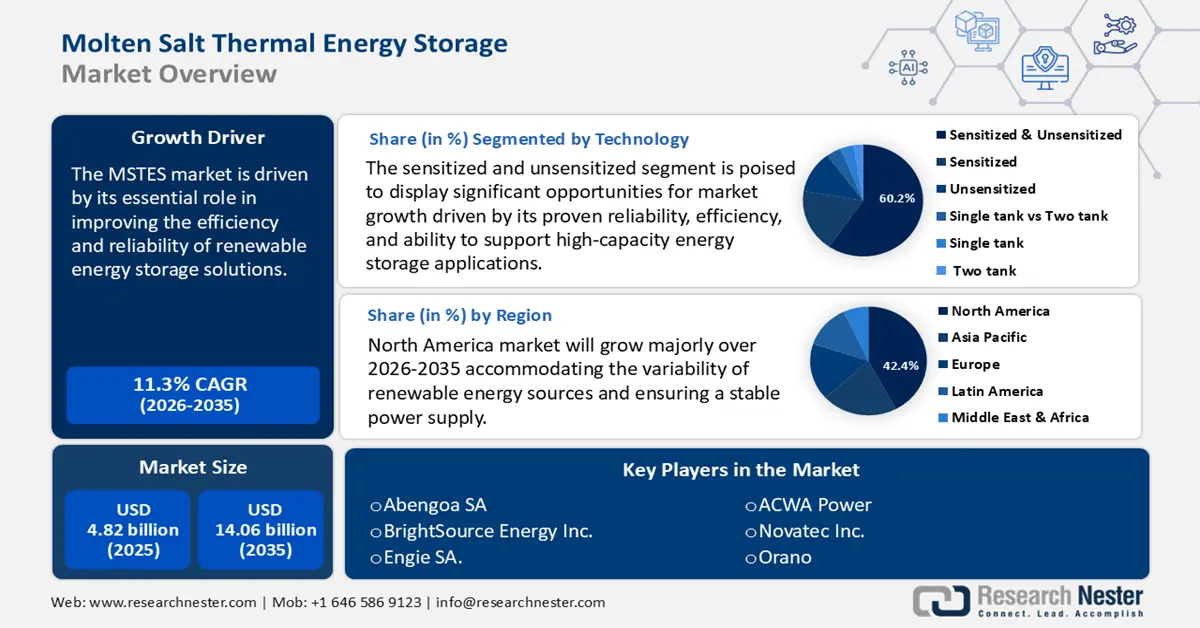
Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Market size was valued at USD 4.82 billion in 2025 and is likely to cross USD 14.06 billion by 2035, registering more than 11.3% CAGR during the forecast period i.e., between 2026-2035. In the year 2026, the industry size of molten salt thermal energy storage is assessed at USD 5.31 billion.
The molten salt thermal energy storage market is witnessing substantial growth, driven by its essential role in improving the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy sources, with rising investments in renewable projects, fueling the demand for stable and efficient energy storage solutions. For instance, in July 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy's Solar Energy Technologies Office (SETO) announced a USD 33 million investment in 9 projects across 7 states, aiming to advance concentrating solar-thermal (CST) systems for solar fuel production and long-duration energy storage.
The demand for MSTES is primarily driven by the global transition towards renewable energy and the necessity for stable, reliable power supplies. Energy storage technologies such as MSTES are pivotal in balancing grid networks and ensuring a consistent power supply, particularly during peak usage periods or when solar generation is low. In September 2023, the U.S. Department of Energy SETO announced USD 30 million for research and development and demonstration projects in thermochemical storage via solar fuel production and local thermal energy storage, with anticipated awards ranging from USD 7.5 billion to USD 10 million.
Opportunities in the molten salt thermal energy storage market are bolstered by international funding and policy support. For instance, in July 2023, Spain's Ministry for the Ecological Transition and the Demographic Challenge (MITECO) launched USD 305.5 million in grants for standalone energy storage projects, including USD 32.74 million specifically allocated for thermal energy storage. These grants aim to accelerate the adoption and integration of energy storage technologies, opening new avenues for market growth and innovation in regions actively promoting renewable energy initiatives.
Key Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Market Insights Summary:
Regional Highlights:
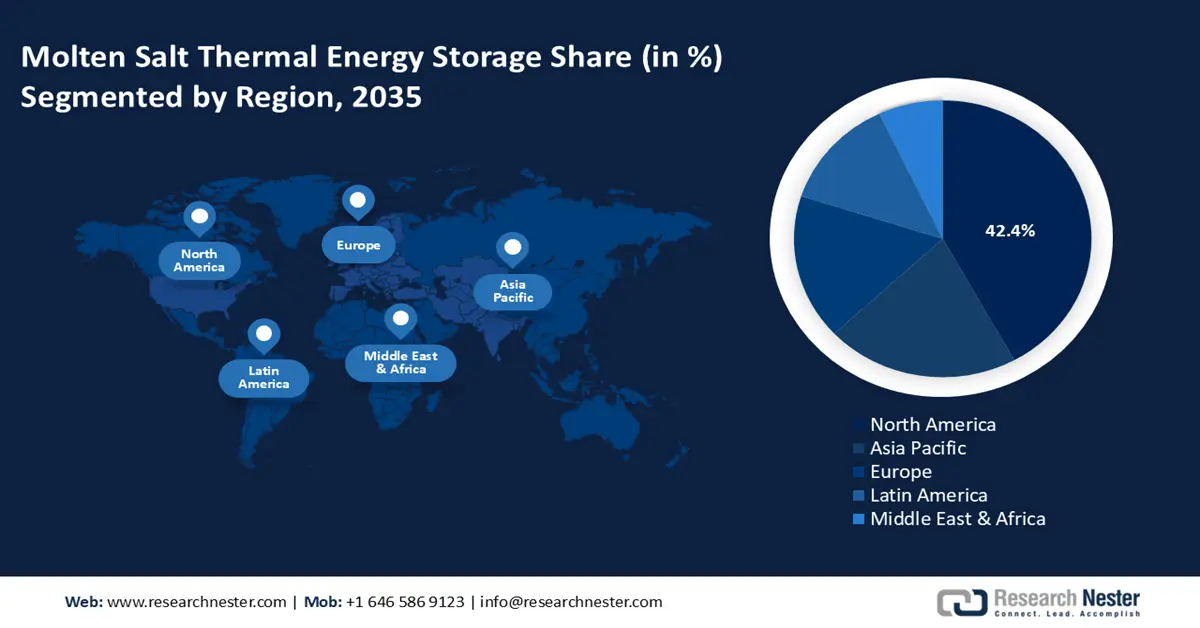
- North America molten salt thermal energy storage market will account for 42.40% share by 2035, driven by established companies investing in R&D enabling early commercial deployment of MSTES projects.
Segment Insights:
- The sensitized and unsensitized segment in the molten salt thermal energy storage market is forecasted to capture a 60.20% share by 2035, influenced by proven reliability and efficiency in large-scale renewable energy storage applications.
- The concentrated solar power plant segment in the molten salt thermal energy storage market is poised for sustainable share by 2035, driven by its ability to provide 24/7 electricity generation using molten salt storage.
Key Growth Trends:
- Increasing demand for new sources of renewable energy
- Service providers reducing carbon emissions to transform the energy sector
Major Challenges:
- High initial investment costs limit market growth
- Technical challenges
Key Players: Acciona S.A., Abengoa SA, BrightSource Energy Inc., SENER Grupo de Ingenieria S.A., SolarReserve LLC.
Global Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Market Forecast and Regional Outlook:
Market Size & Growth Projections:
- 2025 Market Size: USD 4.82 billion
- 2026 Market Size: USD 5.31 billion
- Projected Market Size: USD 14.06 billion by 2035
- Growth Forecasts: 11.3% CAGR (2026-2035)
Key Regional Dynamics:
- Largest Region: North America (42.4% Share by 2035)
- Fastest Growing Region: Asia Pacific
- Dominating Countries: China, United States, Germany, Japan, India
- Emerging Countries: China, India, Japan, South Korea, Chile
Last updated on : 18 September, 2025
Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Market Growth Drivers and Challenges:
Growth Drivers
-
Increasing demand for new sources of renewable energy: The global transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy is accelerating due to multiple pressing challenges, including deleting fossil fuel reserves, rising energy demand, and growing environmental concerns. The increasing frequency of extreme weather events, driven by climate change, has intensified the urgency to reduce carbon emissions and adopt cleaner energy sources. Additionally, geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruption have exposed the vulnerabilities of fossil fuel dependence, promoting nations to seek energy security through renewable alternatives.
Government policies, such as carbon taxes and incentives for green energy projects, further support this shift. For instance, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022 in the U.S. introduced substantial tax credits for clean energy manufacturing, encompassing components essential for TES systems. These incentives aim to stimulate investment in renewable energy infrastructure and minimize carbon emissions. Technological advancements and declining costs in renewable energy and storage solutions, like molten salt thermal energy storage, are making these alternatives more viable, ensuring a stable and sustainable energy supply for the future. Several companies are incorporating power towers into their green energy projects, particularly concentrated solar power (CSP), transmission infrastructure, and hybrid renewable energy systems. For instance, China Xinhupa Power Generation Company initiated a 1 GW solar energy project in July 2022, incorporating a 100 MW tower of CSP with molten salt storage, capable of providing 8 hours of energy storage. Such projects exemplify the rapid adoption of MSTES technologies, underscoring their critical role in the evolving energy landscape.
As the need for dependable energy storage solutions grows, molten salt thermal power plants have emerged as crucial elements in enhancing large-scale solar power facilities.Significant investments from regional and international organizations are anticipated to accelerate advancements in the energy sector. For instance, Rio Tinto's 20-year agreement with Edify Energy aims to supply renewable energy to its Gladstone aluminum operations, significantly reducing reliance on traditional energy sources. Additionally, the increasing power requirement of the industrial sectors is projected to further propel the growth of the molten salt thermal energy storage market during the forecast period. - Service providers reducing carbon emissions to transform the energy sector: The current energy infrastructure faces several critical challenges that drive service providers to innovate and reduce carbon emissions, thereby transforming the energy sector. One significant issue is the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into the existing grid, which necessitates advanced energy storage solutions to maintain stability and reliability.
Additionally, outdated computer systems and infrastructure can hinder the optimal use of battery storage, leading to inefficiencies and increased reliance on fossil fuels. To address these challenges, companies such as Kyoto Group are developing MSTES systems, such as the Heatcube, which stores renewable energy as heat in molten salts for later use, thereby stabilizing the grid and reducing carbon emissions.
Moreover, the leading thermal energy storage companies such as Kyoto Group, Rondo Energy, SunAmp, Eco-Tech Ceram, Energy Nest, and Antora Energy are pioneering solutions to enhance energy storage and grid reliability. By offering comprehensive engineering, procurement, and construction services, these market participants have the potential to revolutionize the energy industry, making it more sustainable and efficient.
Challenges
-
High initial investment costs limit market growth: The deployment of the MSTES system faces a significant challenge due to high initial investment costs, which limit market expansion. The substantial costs associated with procuring materials such as sodium and potassium nitrate, along with the construction of specialized high-temperature facilities to ensure thermal efficiency, pose financial challenges for widespread adoption and scalability.
Additionally, constructing high-temperature storage facilities demands advanced engineering, specialized equipment, and strong safety measures to maintain operational efficiency and longevity. These costs can be particularly prohibitive for smaller energy producers and regions with limited funding for renewable energy projects, restricting their ability to adopt MSTES technology. - Technical challenges: The widespread adoption of the MSTES system is hindered by several technical challenges. These stems require precise temperature control and efficient transfer mechanisms to maintain optimal performance. Deviations from the required temperature range can lead to the degradation of molten salts, reducing their thermal efficiency and lifespan. Additionally, integrating the MSTES system with existing power generation infrastructure can also be complex and technically demanding, necessitating specialized expertise and advanced engineering solutions.
Furthermore, the disposal of used molten salts poses environmental challenges, as improper disposal can lead to soil and water contamination. Stringent regulatory frameworks governing the construction and operation of energy storage facilities can create additional compliance costs and delays for project developers. These technical and environmental challenges necessitate continuous innovation and cost-reduction efforts within the MSTES sector to enhance its competitiveness and sustainability.
Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Market Size and Forecast:
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
|
CAGR |
11.3% |
|
Base Year Market Size (2025) |
USD 4.82 billion |
|
Forecast Year Market Size (2035) |
USD 14.06 billion |
|
Regional Scope |
|
Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Market Segmentation:
Technology Segment Analysis
Sensitized and unsensitized segment is set to hold over 60.2% molten salt thermal energy storage market share by the end of 2035. The dominance is primarily driven by its proven reliability, efficiency, and ability to support high-capacity energy storage applications, making it a preferred choice for large-scale renewable energy integration. The sensitized and unsensitized heat storage system uses molten salt as a heat storage medium and is widely preferred in large-scale solar thermal power plants for their ability to enable extended energy storage.
By efficiently storing and releasing heat, these systems help stabilize the energy supply, ensuring continuous power generation during periods of low solar radiation. The adoption of sensitized and unsensitized heat storage technology in the molten salt thermal energy storage market is propelled by continuous advancements that enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Notably, the development of novel phase change materials (PCMs) with higher energy density and improved thermal stability has significantly improved TES capacity and efficiency, making them suitable for industrial and residential applications.
The seamless integration of sensitized and unsensitized systems with existing power plan infrastructure further strengthens molten salt thermal energy storage market position, providing energy providers with a cost-effective solution to bolster grid reliability and increase the utilization of renewable energy sources. For instance, the Crescent Dunes Solar Energy Project in Nevada employs molten salt-based sensitized and unsensitized heat storage technology to store solar energy, enabling electricity generation during periods without sunlight and thereby enhancing grid stability. As industries increasingly prioritize sustainable and reliable energy solutions, the dominance of sensitized and unsensitized heat storage in the market is expected to persist, reinforced by its significant market share in 2024 and its proven effectiveness in large-scale energy store applications.
Application Segment Analysis
The Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants segment is projected to account for a sustainable share of the molten salt thermal energy storage market. An advantage of molten salt technology is its capacity to retain high-temperature heat for extended periods, even after sunlight is no longer available. This capability enables CSP facilities equipped with thermal energy storage to generate electricity around the clock, irrespective of weather conditions or time of day. For instance, the Solana Generating Station in Arizona uses molten salt-based thermal energy storage to store solar heat during daylight hours, allowing for electricity production during nighttime or cloudy periods, thereby enhancing grid stability and ensuring a consistent power supply.
MSTES systems offer multi-hour storage capabilities, effectively balancing the intermittent nature of solar irradiance and meeting the baseload power demand for the electric grid. This technology eliminates the necessity for natural gas backups, enabling uninterrupted power supply and paving the way for 24/7 carbon-free solar energy, Consequently, molten salt storage has become a standard feature in the new CSP project worldwide. For instance, the Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) 700 MW CSP project incorporates molten salt thermal energy storage to provide continuous power generation, enhancing grid reliability and supporting renewable energy goals.
In contrast, residential and industrial heat applications typically do not require around-the-clock energy availability. Residential energy consumption is often lower during nighttime, reducing the necessity for a continuous energy supply. Similarly, many industrial processes operate on schedules that do not demand 24/7 energy input, allowing for planned downtime and maintenance periods. Therefore, while molten salt storage is integral to utility-scale solar power generation, its application in residential and industrial heat scenarios is less critical due to differing demand patterns.
Our in-depth analysis of the global molten salt thermal energy storage market includes the following segments:
|
Technology |
|
|
Application |
|

Vishnu Nair
Head - Global Business DevelopmentCustomize this report to your requirements — connect with our consultant for personalized insights and options.
Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Market Regional Analysis:
North America Market Insights
In molten salt thermal energy storage market, North America region is predicted to capture over 42.4% revenue share by 2035. This leadership is largely attributed to the presence of established companies in the U.S. that have invested heavily in research and development, enabling the early commercial deployment of MSTES projects. Such advancements have provided utilities and large industrial players with innovative storage solutions essential for balancing the grid amidst the increasing integration of renewable energy sources.
A favorable policy environment that promotes renewable energy adoption, coupled with incentives for research, has further facilitated the scaling up of molten salt technology in the region. For instance, in West Texas, Natural Resources and Abilene Christian University (ACU) are constructing a molten salt research reactor aimed at addressing water and energy challenges. Partnering with Texas Tech, the project plans to integrate this reactor technology with desalination processes. The reactor, operating at over 600 degrees Celsius, can generate 250 megawatts of clean energy and aid in desalinating water, a critical resource in Texas. These strategic initiatives underscore North America's commitment to advancing MSTES technologies, thereby reinforcing its molten salt thermal energy storage market dominance and supporting the transition toward a more sustainable energy future.
On the other side, the Canada molten salt thermal energy storage market is also poised for growth during the forecast period, as the country seeks to diversify its energy storage solutions to support a resilient and substantial energy grid. The adoption of MSTES in Canada aligns with its objectives to increase renewable energy capacity and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. While specific large-scale MSTES projects in Canada are in the development stages, the country's favorable policy environment and investment in renewable energy research indicate a growing interest in deploying such technologies soon.
Both the U.S. and Canada recognize the potential of MSTES to provide long-duration energy storage, which is essential for accommodating the variability of renewable energy sources and ensuring a stable power supply. As these technologies mature and become more cost-effective, it is anticipated that MSTES will play a significant role in the energy strategies of both countries.
Asia Pacific Market Insights
The Asia Pacific region is expected to witness a growth rate in the molten salt thermal energy storage market, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing energy demand in countries like China and India. This growth is driven by the need to integrate renewable energy sources into the grid and enhance energy security. China is actively developing MSTES projects to support its renewable energy initiatives. Notably, a 100mW thermal solar and molten salt energy storage system is under construction in Xinjiang, aiming for completion and grid connection by the end of 2024. This project is part of a larger 1 GW solar thermal energy + photovoltaic integration initiative, reflecting China's commitment to large-scale renewable energy integration.
India rapid industrialization and increasing energy demand have prompted the exploration of MSTES technologies. The country's vast solar potential makes MSTES an attractive option for providing stable, baseload power. A notable instance is the Gujarat Solar One 25 MW CSP plant stands as India's largest parabolic trough CSP plant, featuring a molten salt storage capacity that allows for 9 hours of energy retention. The plant employs a two-tank indirect thermal energy storage system, underscoring India's commitment to integrating MSTES solutions to enhance the reliability and efficiency of its renewable energy infrastructure.
Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Market Players:
- Yara International ASA
- Company Overview
- Business Strategy
- Key Product Offerings
- Financial Performance
- Key Performance Indicators
- Risk Analysis
- Recent Development
- Regional Presence
- SWOT Analysis
- Acciona S.A.
- Abengoa SA
- BrightSource Energy Inc.
- SENER Grupo de Ingenieria S.A.
- SolarReserve LLC
- Engie SA
- ACWA Power
- KVK Energy Ventures Ltd.
- Novatec Inc.
- Orano
Leading players in the molten salt thermal energy storage market are actively investing in product development to increase their market presence. Major companies are also pursuing strategic partnerships and acquisitions to expand their customer base and geographical reach.
Recent Developments
- In January 2025, Hyme Energy, a frontrunner in thermal energy storage solutions, partnered with Arla, a prominent global dairy manufacturer, to create the largest industrial thermal storage system in the world. This initiative, designed for Arla’s milk powder production facility located in Holstebro, Denmark, seeks to achieve economical reductions in CO2 emissions associated with industrial heat generation and represents a crucial advancement in Hyme’s path toward commercialization.
- In May 2024, the Saudi Arabian oil company Aramco signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with Rondo Energy, a company specializing in thermal energy storage, after making an equity investment. The two organizations have initiated engineering studies aimed at implementing Rondo’s Heat Battery technology on an industrial scale to lower emissions at Aramco's facilities, with plans to eventually expand to a capacity of 1GWh.
- Report ID: 7403
- Published Date: Sep 18, 2025
- Report Format: PDF, PPT
- Explore a preview of key market trends and insights
- Review sample data tables and segment breakdowns
- Experience the quality of our visual data representations
- Evaluate our report structure and research methodology
- Get a glimpse of competitive landscape analysis
- Understand how regional forecasts are presented
- Assess the depth of company profiling and benchmarking
- Preview how actionable insights can support your strategy
Explore real data and analysis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Market Report Scope
Free Sample includes current and historical market size, growth trends, regional charts & tables, company profiles, segment-wise forecasts, and more.
Connect with our Expert
Copyright @ 2026 Research Nester. All Rights Reserved.




