Low-cost Carrier Market Outlook:
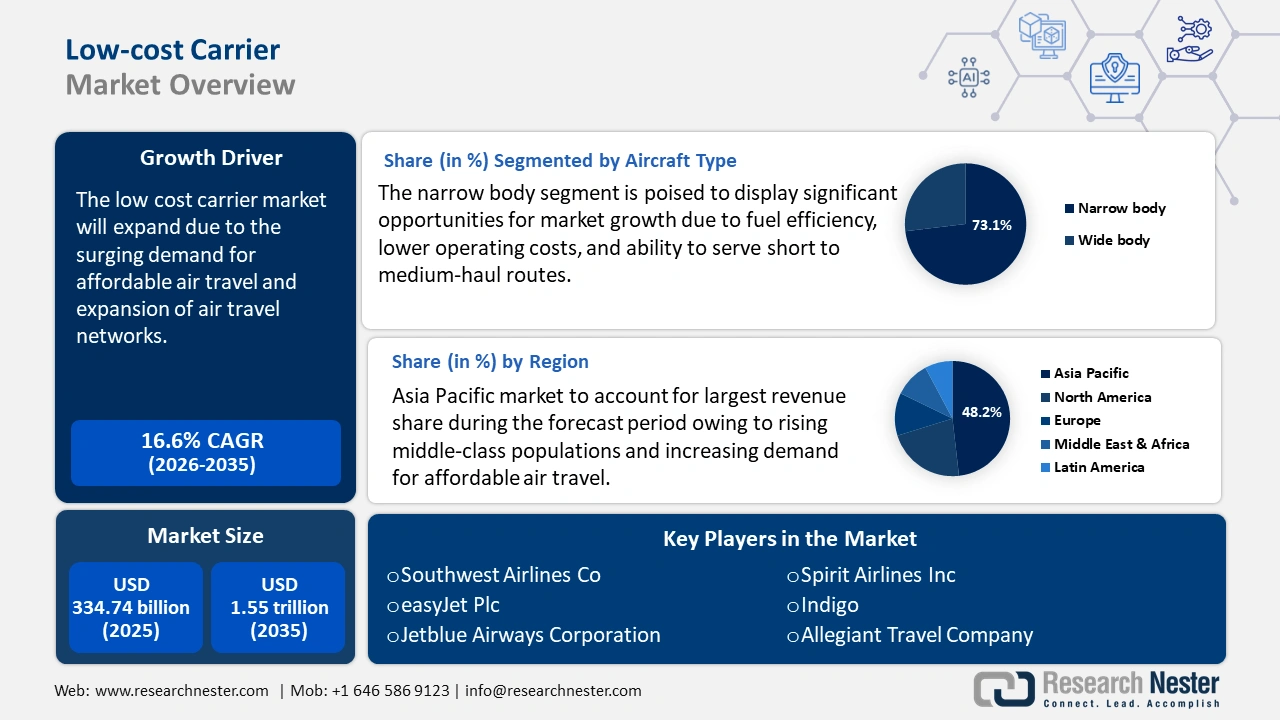
Low-cost Carrier Market size was over USD 334.74 billion in 2025 and is poised to exceed USD 1.55 trillion by 2035, witnessing over 16.6% CAGR during the forecast period i.e., between 2026-2035. In the year 2026, the industry size of low-cost carrier is estimated at USD 384.75 billion.
The low-cost carrier (LCC) market has experienced substantial growth owing to the rising demand for affordable air travel. The rising middle-class population and disposable income especially in emerging markets have led to demand for low-cost air travel. The International Air Transport Association (IATA) states that passenger numbers are expected to reach 5.2 billion in 2025, marking a 6.7% rise compared to 2024. LCCs produce around 33% of all scheduled airline seats in a week and operate 30% of all scheduled flights. This makes the low-cost carrier market the fastest-growing sector in recent years. Further, in the global space, LCCs are known to operate one-third of all airline seats. Out of 741 flights operating weekly, 114 airlines are LCCs. A report by the World Bank Group suggests that the introduction of LCCs has not only brought lower fares to the air transport market but has also contributed to countries’ economies.
Low-cost carriers adopt an unbundled pricing approach offering basic fares and charging separately for additional services. This model allows passengers to customize their travel experience while enabling airlines to generate extra income. Low-cost carriers maximize profits through extra charges for baggage, seat selection, meals, and onboard entertainment. It generates additional revenue from advertising frequent loyalty programs and partnerships with hotels and rental services that add additional revenue streams. For instance, in 2022, Spirit Airlines reported an ancillary revenue of USD 67.61 per person contributing 54.3% of its total revenue. This highlights the effectiveness of ancillary services driving the demand for low-cost carrier markets.
Key Low-cost Carrier Market Insights Summary:
Regional Highlights:
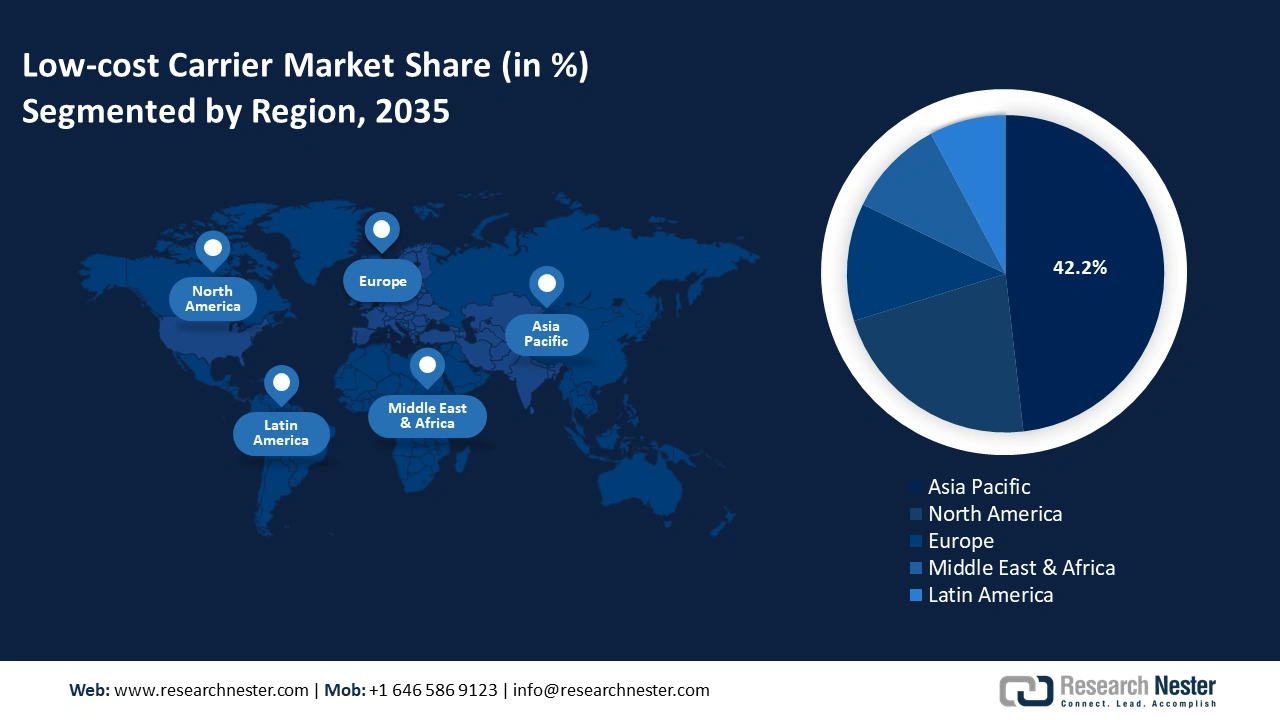
- Asia Pacific low-cost carrier market will account for 48.20% share by 2035, driven by rising middle-class population and increasing demand for affordable air travel.
- North America market grows rapidly CAGR during the forecast period 2026-2035, driven by increasing demand for budget-friendly travel and aggressive expansion of low-cost carrier airlines.
Segment Insights:
- The narrow-body aircraft segment in the low-cost carrier market is expected to command a 73.10% share by 2035, driven by narrow-body aircraft's fuel efficiency, lower operating costs, and suitability for short- to medium-haul routes.
- The commercial application segment in the low-cost carrier market is anticipated to capture significant share by 2035, driven by rising global demand for affordable air travel supported by expanding commercial aviation operations.
Key Growth Trends:
- Expansion of air travel networks
- Increasing digitalization and technology adoption
Major Challenges:
- Rising fuel costs
- Intense competition and market saturation
Key Players: Southwest Airlines Co., AirAsia Group Berhad, easyJet plc, JetBlue Airways Corporation, Norwegian Air Shuttle ASA, Spirit Airlines, Inc., IndiGo and Wizz Air Holdings plc.
Global Low-cost Carrier Market Forecast and Regional Outlook:
Market Size & Growth Projections:
- 2025 Market Size: USD 334.74 billion
- 2026 Market Size: USD 384.75 billion
- Projected Market Size: USD 1.55 trillion by 2035
- Growth Forecasts: 16.6% CAGR (2026-2035)
Key Regional Dynamics:
- Largest Region: Asia Pacific (48.2% Share by 2035)
- Fastest Growing Region: Asia Pacific
- Dominating Countries: United States, China, Germany, Japan, United Kingdom
- Emerging Countries: China, India, Japan, South Korea, Thailand
Last updated on : 18 September, 2025
Low-cost Carrier Market Growth Drivers and Challenges:
Growth Drivers
- Expansion of air travel networks: Low-cost carrier companies are adding new domestic and international routes to increase accessibility. More secondary and regional airports are becoming operational, reducing congestion at major hubs. Some LCCs are expanding into long-haul routes using fuel-efficient aircraft such as the Airbus A321XLR and Boeing 787. For instance, in January 2025 Norse Atlantic Airways, a low-cost Norwegian carrier introduced a new direct flight between Greece and the U.S. This new route will be operational from June 3, 2025, offering four weekly flights between Los Angeles, California, USA, and Athens, Greece. This new direct flight provides an affordable way to travel between Los Angeles and Athens with fares starting from USD 269 one-way. The flights will be operated on Boeing 787 Dreamliners, providing a comfortable and efficient long-haul travel experience.
- Increasing digitalization and technology adoption: Mobile apps and AI-driven pricing help optimize the revenue of low-cost carrier planes. Moreover, automated check-ins and self-service kiosks reduce overall operational costs. Online direct booking reduces reliance on third-party agencies. Low-cost carriers are increasingly focusing on direct online booking platforms to reduce reliance on intermediaries and enhance personalized services. By encouraging passengers to book directly through their websites and mobile apps, LCCs minimize commission expenses associated with third-party travel agencies. For instance, the World Bank Report states that the cost per booking via an airline’s system is estimated at around USD 1, whereas the cost per booking via a global distribution system (GDS) is between USD 5 and USD 12. This strategy not only lowers costs but also allows airlines to collect valuable customer data to tailor marketing efforts and service offerings to individual preferences.
Challenges
- Rising fuel costs: Fuel is the largest operating expense for low-cost carriers, making up 30-40% of total costs. Unlike full-service airlines, low-cost carriers have limited ability to hedge fuel prices due to financial constraints. When fuel prices rise, LCCs have limited options to pass costs to passengers as the business model depends on offering the lowest fares.
- Intense competition and market saturation: The low-cost carrier (LCC) market is highly competitive with many airlines fighting for the same price-sensitive customers. Price wars among competitors lead to lower profit margins making it difficult for airlines to sustain long-term profitability. To handle this, major full-service airlines have launched their budget subsidiaries such as Singapore Airline Scoot, and Qantas Jetstar to increase competition.
Low-cost Carrier Market Size and Forecast:
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
|
CAGR |
16.6% |
|
Base Year Market Size (2025) |
USD 334.74 billion |
|
Forecast Year Market Size (2035) |
USD 1.55 trillion |
|
Regional Scope |
|
Low-cost Carrier Market Segmentation:
Aircraft Type Segment Analysis
By 2035, narrow-body segment is expected to dominate over 73.1% low-cost carrier market share. Narrow-body aircraft are the backbone of low-cost carriers due to their fuel efficiency, lower operating costs, and ability to serve short to medium-haul routes. These aircraft enable low-cost carriers to maintain high utilization rates, quick turnaround, and cost-effective operations. More low-cost carriers are shifting towards next-generation narrow-body jets which offer greater range and better fuel efficiency. For instance, in July 2024 Air India announced the launch of its first narrow-body aircraft A320 Neo in Delhi. The new aircraft boasts a three-class configuration, including luxurious business class seats, 24 premium economy seats with extra legroom, and 132 economy class seats.
Application Segment Analysis
The commercial segment is anticipated to hold a significant low-cost carrier market share through 2035. The growth of commercial aviation can be attributed to increasing air travel demands globally due to low-cost carriers offering affordable air travel. According to the Air Transport Action Group Report, 35.3 million scheduled commercial flights took place in 2023 with airports handling some 96 million aircraft movements. Additionally, in 2023, 1,138 airlines operated a fleet of 29,039 commercial aircraft in service. With 4,072 airports globally and scheduled commercial flights in the world, it is evident that the commercial segment can grow at a robust pace in the coming years.
Our in-depth analysis of the global low-cost carrier (LCC) market includes the following segments:
|
Aircraft Type |
|
|
Application |
|
|
Distribution Channel |
|
|
Operations |
|

Vishnu Nair
Head - Global Business DevelopmentCustomize this report to your requirements — connect with our consultant for personalized insights and options.
Low-cost Carrier Market Regional Analysis:
Asia Pacific Market Insights
By 2035, Asia Pacific low-cost carrier market is likely to hold more than 48.2% share, driven by rising middle-class population and increasing demand for affordable air travel. Countries such as India, China, and Southeast Asian nations are the key markets with Indigo, AirAsia, and Scoot expanding their networks. Low-cost carrier (LCC) markets in the region offer a wide range of short and medium-haul flights leveraging cost efficiencies and high aircraft utilization. Competitive pricing and flexible service models have made these carriers a preferred choice for budget-conscious travelers.
The low-cost carrier model in China has seen significant growth due to rising demand for passenger and cargo air travel. As income levels increase and the middle class expands in second and third-tier cities in China, the demand for low-cost air travel options will significantly increase. The low-cost carrier market in China is characterized by short-haul flights with efficient operations to keep costs low. According to Boeing’s press release of 2024, air travel in China is expected to grow 5.2% annually, creating the world's largest traffic market. It is further anticipated that rising passenger volumes will boost the low-cost carrier market as airlines plan to grow their networks by connecting major hubs to smaller cities. For instance, in January 2025, China Southern Airlines announced plans to resume its Shenzhen-Tokyo Narita service in February 2025, utilizing the Airbus A321neo. This route restoration aims to reconnect major international destinations as global air travel demand continues to rise.
India ranks no. 1 among the top 10 countries with the highest share of low-cost carriers in overall airline capacity. Travellers are prioritizing cost-effective options, leading to a shift from full-service airlines to low-cost carriers. IATA reports state that India is expected to overtake China and the U.S. as the world's third-largest air passenger market by 2030. Further, the rising demand in the aviation sector has pushed the number of airplanes operating in the sector. The number of airplanes is expected to reach 1,100 planes by 2027. The rapid increase in passenger numbers driven by urbanization and economic growth is accelerating the expansion of low-cost carrier market in India.
North America Market Insights
North America in low-cost carrier market is anticipated to expand at a rapid pace from 2026 to 2035 attributed to increasing demand for budget-friendly travel, especially for domestic and leisure routes. Airlines such as Southwest, Spirit, and Frontier have expanded aggressively offering low fares with optional add-ons to attract cost-conscious travelers. Further, rising competition with legacy carriers has pushed LCCs to innovate with ultra-low-cost models and loyalty programs. The growth of secondary airports and point-to-point networks allows LCCs to reduce operational costs and serve more destinations efficiently.
The Low-cost carrier (LCC) market in the U.S. is growing due to increasing demand for affordable travel amid rising ticket prices from legacy airlines. For instance, Spirit Airlines often provides fares that are 30-50% lower than full-service carriers on similar routes. The rise of ultra-low-cost models where passengers pay only for essential services has attracted a wider customer base. Additionally, the post-pandemic travel surge and a shift towards domestic leisure travel have fueled the growth of LCCs in the U.S. For instance, in 2020 JetBlue launched new direct flights from New York to Guadeloupe, appealing to most cost-conscious leisure travellers.
The low-cost carrier (LCC) market in Canada is experiencing steady growth as travellers seek more affordable alternatives to the country’s traditionally high airfares. Airlines such as Flair Airlines and Lynx Air have highly expanded challenging legacy carriers Air Canada and West Jet with budget-friendly domestic and trans-border routes. Additionally, limited rail infrastructure in Canada makes air travel essential, boosting demand for low-cost carrier services. Moreover, secondary airports such as Hamilton and Abbotsford allow low-cost carriers to reduce operational costs and offer lower fares.
Low-cost Carrier Market Players:
- Southwest Airlines Co.
- Company Overview
- Business Strategy
- Key Product Offerings
- Financial Performance
- Key Performance Indicators
- Risk Analysis
- Recent Development
- Regional Presence
- SWOT Analysis
- AirAsia Group Berhad
- easyJet plc
- JetBlue Airways Corporation
- Norwegian Air Shuttle ASA
- Spirit Airlines, Inc.
- IndiGo
- Wizz Air Holdings plc
- Allegiant Travel Company
Low-cost carriers have reshaped global air travel by making flying more accessible and affordable. The low-cost carrier market is dominated by several major airlines across different regions each offering cost-efficient operations and budget friendly pricing strategies. Southwest Airlines leads in the U.S. by offering a point-to-point network and free checked bags, while Spirit Airlines follows a very low-cost model with add-on services. Indigo, India’s largest LCC capitalizes on the country’s growing domestic demand while Air Asia dominates Southeast Asia with extensive regional connectivity. Here are some leading players in the low-cost carrier market:
Recent Developments
- In October 2024, low-cost carrier Norse Atlantic Airways announced a new direct service between Rome and Los Angeles for the 2025 summer season. The new service will operate three times a week from 22nd May 2025. This move is a growth strategy as the carrier aims to grow its transatlantic network in response to increasing demand. The one-way fares will be starting from USD 199 between Los Angeles and Rome, including taxes.
- In June 2024, Air Asia was awarded the World’s Best Low-Cost Airline at the Skytrax World Airline Awards 2024, marking a historic win for the 15th consecutive year. This achievement is driven by AirAsia's continuous pursuit of innovation and value creation within the low-cost carrier segment.
- Report ID: 7209
- Published Date: Sep 18, 2025
- Report Format: PDF, PPT
- Explore a preview of key market trends and insights
- Review sample data tables and segment breakdowns
- Experience the quality of our visual data representations
- Evaluate our report structure and research methodology
- Get a glimpse of competitive landscape analysis
- Understand how regional forecasts are presented
- Assess the depth of company profiling and benchmarking
- Preview how actionable insights can support your strategy
Explore real data and analysis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Low-cost Carrier Market Report Scope
Free Sample includes current and historical market size, growth trends, regional charts & tables, company profiles, segment-wise forecasts, and more.
Connect with our Expert
Copyright @ 2026 Research Nester. All Rights Reserved.




