Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction Treatment Market Outlook:
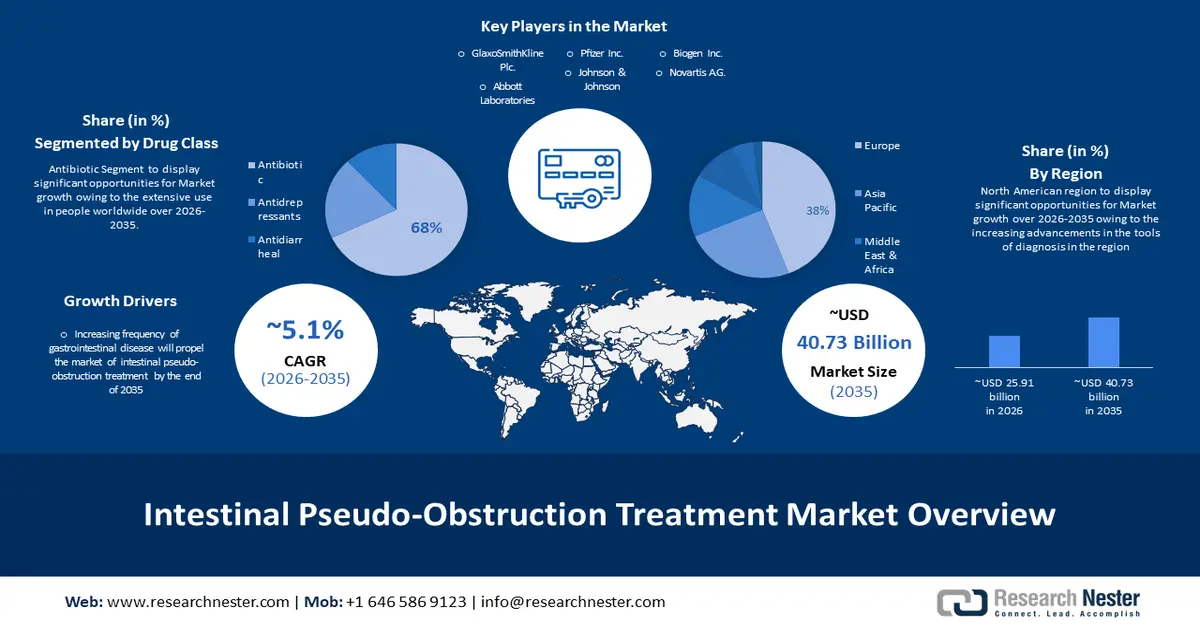
Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction Treatment Market size was over USD 24.77 billion in 2025 and is poised to exceed USD 40.73 billion by 2035, witnessing over 5.1% CAGR during the forecast period i.e., between 2026-2035. In the year 2026, the industry size of intestinal pseudo-obstruction treatment is estimated at USD 25.91 billion.
The increased frequency of gastrointestinal disease will propel the primary reason behind the growth of the intestinal pseudo-obstruction treatment market. As the macroeconomic prospect degenerates for the automotive industry, a modest return to expansion is anticipated for the latest clients and commercial vehicle sales in the next two years. It is projected that international vehicle sales will expand by 5.1% in 2023 and 3.6% in 2024. Moreover, automakers can project sales to come back to the 90 million+ high water mark in 2025.
Another reason that will propel the intestinal pseudo-obstruction treatment market by the end of 2036 is the cost-effective diagnosis and treatment worldwide. Patient existence was 89% at 1 year and 69% at 5 years with corresponding graft existence of 87% and 56%. Retransplantation was victorious in 86%. The primary treatment is wholesome support to stop malnutrition and antibiotics to cure bacterial infections. ailments that may coexist and deteriorate symptoms of pseudo-obstruction--like gastroparesis (postponed stomach emptying), gastroesophageal reflux, or bacterial gigantism—require to be recognized and cured. The challenges of curing chronic pseudo-obstruction are repeatedly many-sided and comprise the patient and family along with the physician. The physician may recommend a multidisciplinary technique for therapy. A maintenance team might comprise the child's pediatric gastroenterologist, a pediatric pain maintenance specialist, a behavioral expert, and others. In acute cases, surgery to eliminate part of the intestines might be important. In a subset of patients, when pseudo-obstruction is restricted to an isolated segment of the bowel, surgical bypass may be acknowledged. In the most severe cases, when patients getting total parenteral nutrition undergo life-threatening problems like severe infection or liver failure, small bowel relocation may be acknowledged. This technique is challenging and has a lot of related risks. It should only be acknowledged when all other therapy choices have been worn out.