Blood Group Typing Market Outlook:
Blood Group Typing Market size was over USD 2.3 Billion in 2025 and is poised to exceed USD 5.55 Billion by 2035, witnessing over 9.2% CAGR during the forecast period i.e., between 2026-2035. In the year 2026, the industry size of blood group typing is estimated at USD 2.49 Billion.
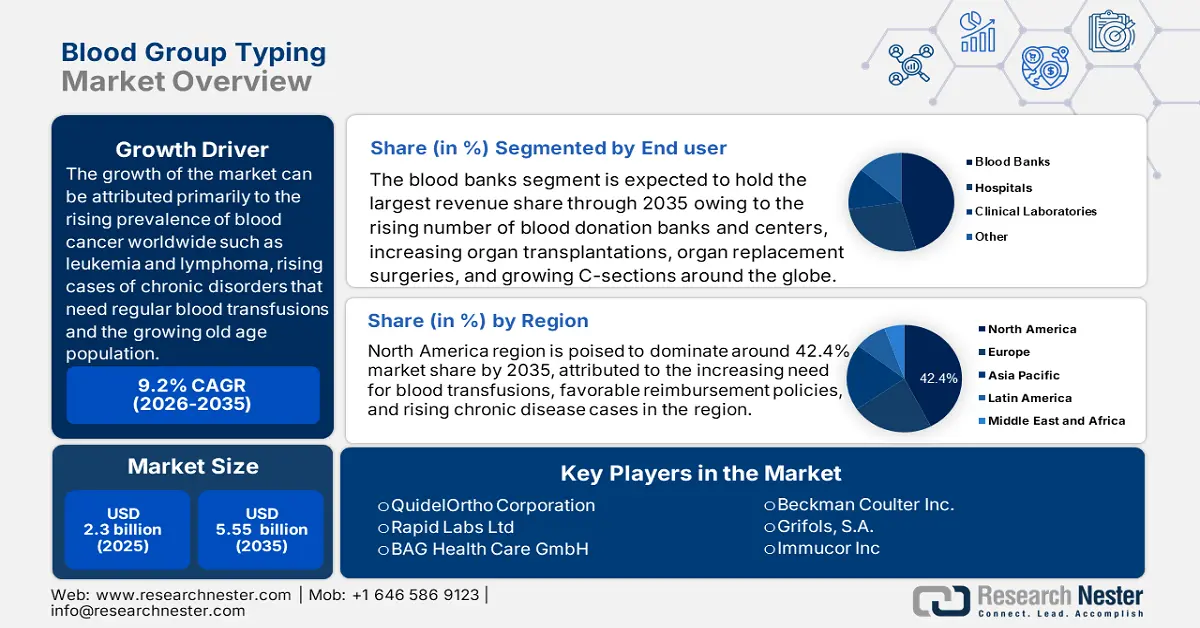
The growth of the market can be attributed primarily to the rising prevalence of blood cancer worldwide such as leukemia and lymphoma, rising cases of chronic disorders that need regular blood transfusions such as anemia, and cancer, and the growing old age population as bone marrow of geriatrics cannot replenish blood that is lost. The rising prevalence of these diseases is anticipated to generate a high demand for blood group typing in the healthcare sector. According to the American Cancer Society, in the year 2022, 60,650 new cases of leukemia were diagnosed, 24,000 people died from leukemia, and 20,050 cases of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) were reported in the United States.
In addition to the aforementioned factor, the rise in the number of donations across the world is estimated to increase blood group typing procedures in the healthcare sector. Also, the high prevalence of accidents, injuries, and trauma that led to massive blood transfusion as a treatment is anticipated to bring more positive opportunities for the blood group typing market over the next years. Moreover, rising demand for blood and blood-related products, the emergence of advanced technologies, growing awareness of early disease diagnosis and screening, and the growing need for safe blood transfusions, coupled with a rise in blood donations worldwide, are expected to drive global blood group typing market growth during the forecast period. Approximately 40% of the 118.5 million blood donations collected worldwide are collected in high-income countries, home to 16% of the world's population, according to World Health Organization data. Furthermore, the global market is projected to witness steady growth over the analysis period on the account of the development of automated blood typing technologies such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) which is based on microarray techniques that have enhanced the speed of transfusion diagnostics along with its standardization and safety.