Aspirin Exacerbated Respiratory Disease Market Outlook:
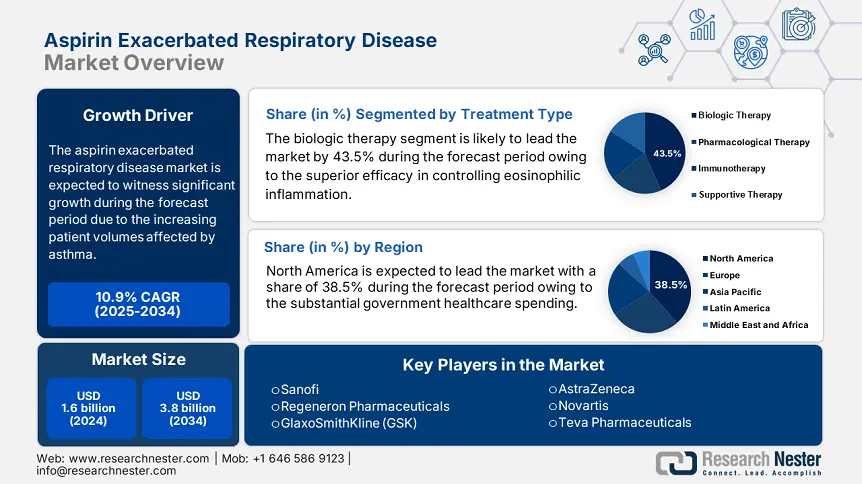
Aspirin Exacerbated Respiratory Disease Market size was valued at USD 1.6 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 3.8 billion by the end of 2034, rising at a CAGR of 10.9% during the forecast period, 2025 to 2034. In 2025, the industry size of aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease is estimated at USD 1.7 billion.
The global aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease market is rising rapidly and is fueled by increasing patient volumes affected by asthma. Most people affected by asthma disease have 8% to 11% impact on aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease, mainly those with comorbid chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis. As per the CDC report, 25.6 million people in the U.S. are estimated to have asthma in 2023, and 1.9 million to 2.7 million people are expected to have aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease in the U.S. The NIH has reported that aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease is a severe disease caused by severe asthma, qualifying it for inclusion in multiple federally funded therapeutic trials and research.
A multi-stage international supply chain is used to produce drugs and biologics for AERD therapy, particularly corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, and monoclonal antibodies. API synthesis is mostly done in China and India, bulk drug production is done in Europe and the U.S., and final product formulation and assembly are carried out in facilities with GMP certification throughout the EU and North America. The producer price index has increased by 5.2% in 2024 for pharmaceutical preparations, and the consumer price index has risen to 2.9% for medical care commodities. These values impact the demand for drugs related to respiratory such as biologics used in managing AERD. On the import side, as per the U.S. International Trade Commission data, nearly 3.5 billion API related to respiratory APIs in the U.S., with 30.2% imported from China and 40.5% from India. These trades enhance the supply environment in the aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease globally.