Anti-Caking Agent Market - Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific Market Insights
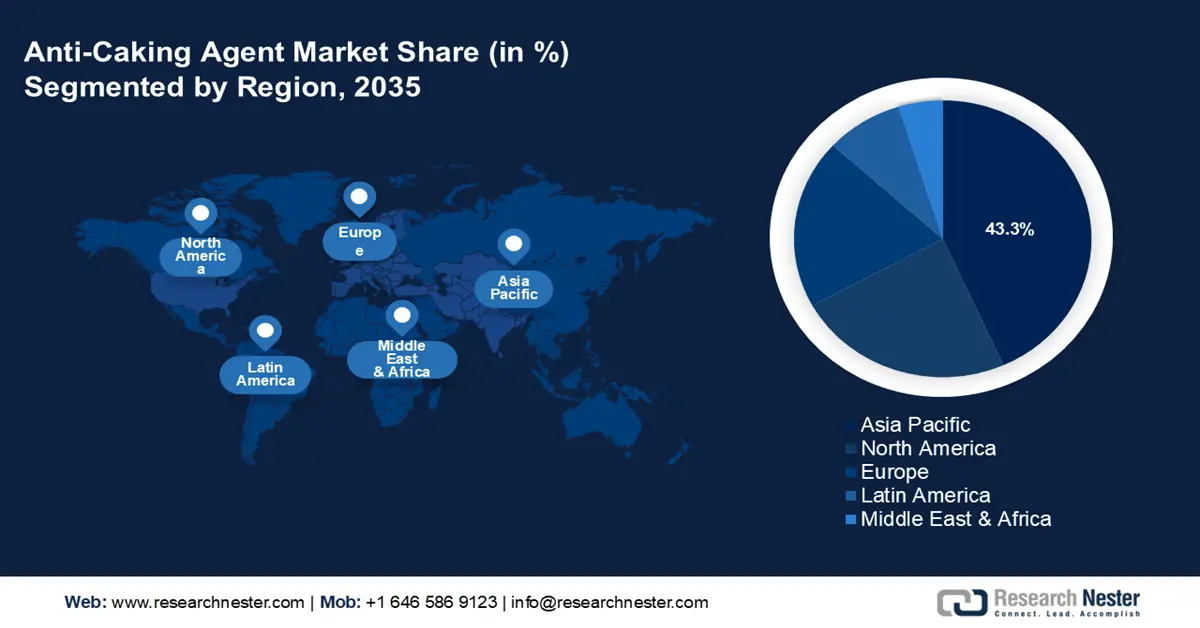
Asia-Pacific is anticipated to dominate the global anti-caking agent market with the largest revenue share of 43.3% by 2035, driven by its swift industrial development and the growth of its food processing sector. This notable market position is fueled by the rising demand in nations such as China and India, where the increasing consumption of packaged and processed foods is consistently enhancing the utilization of anti-caking agents across multiple sectors, including food, agriculture, and chemicals. In 2024, clean energy consumption in China increased to 28.6% of the total energy consumption, an increase of 2.2% points compared to the previous year, which shows the increasing pressure on regulations and changes in infrastructural patterns that favor sustainable chemical production. In the meantime, the sourcing of sulphuric acid (100%) in China rose by 6.9% in 2024 compared to 2023, indicating that the chemical raw materials industry is growing. These trends in both chemicals/raw materials and the usage of cleaner energy in APAC are the basis of expected demand in the case of the anti-caking agent because food, pharma, and industrial industries need better stability and adherence to environmental standards.
China anti-caking agent market is set to lead the region with the highest revenue share by 2035, driven by swift industrialization, stringent sustainability requirements, and government incentives that encourage green chemical technologies. The 2023 policy reforms from the Ministry of Ecology and Environment promote cleaner production practices, while ChemChina's investments in sustainable manufacturing increase capacity. Furthermore, China's extensive chemical manufacturing infrastructure facilitates economies of scale, thereby enhancing the demand for anti-caking agents in the food, pharmaceutical, and industrial sectors. Moreover, China has recorded objective progress in environmental control, as in 2024, the average amount of PM2.5 in 339 large cities was 29.3 micrograms per cubic meter, which is reduced by 2.7% each year, and it is below the interim level of 35 mcg/ cubic meter.
India’s anti-caking agent market is projected to grow substantially over the forecast period from 2026 to 2035, owing to the expanding food processing industry, which is a direct driver of demand for anti-caking agents in the powdered, granulated, and dry mix products. The food processing market is expected to increase its production to USD 535 billion in the FY 2025-26. The industry has a manufacturing contribution of approximately 7.7% and currently has a population of more than 7 million individuals in the value chain. Even the chemicals sector of India (anti-caking agents represent one of its subcategories) is worth approximately USD 220 billion, as of 2023, and declines to approximately USD 40 billion by 2026. Furthermore, the export of processed food in the Fiscal Year 2023-24 in India was estimated to be USD 10.88 billion, which makes up 23.4% of the total agri-food exports of an estimated USD 46.4 billion. It means that the processed food industry is developing tremendously, and its percentage of agri-food exports grew to 23.4% in FY 2023-24 compared to 13.7% in FY 2014-15. Therefore, the increase in food processing volumes, the development of the chemical industry, and the unambiguous regulation leave make the Indian anti-caking agent market grow steadily.
North America Market Insights
The North American market is projected to account for 23.7% of the global anti-caking agent market, propelled by a growing demand within the pharmaceuticals and food sectors. Significant trends encompass a heightened regulatory emphasis on sustainable chemical manufacturing and innovations that receive backing from federal funding. Government initiatives that advocate green chemistry and chemical safety contribute to the expansion of the market. Furthermore, the burgeoning clean energy chemical industry stimulates investments in advanced manufacturing processes and adherence to environmental regulations. Furthermore, in 2023, the U.S. Department of Energy allocated USD 78 million to the decarbonization of the chemicals manufacturing sector, including the development of process intensification and cleaner reactor technologies. Meanwhile, the DOE also announced an open funding of USD 150 million in 2022 to conduct research in order to reduce carbon emissions in manufacturing and energy technologies. Such investments lower the cost pressures and assist the manufacturers to meet the higher environmental regulations, which consequently favors the increased demand of anti-caking agents manufactured using cleaner and more sustainable practices in North America.
The anti-caking agent market in the U.S. is expected to lead the North American market with the largest revenue share over the projected years, driven by the increased demand for processed and packaged foods, which, in large part, are dependent on the use of additives to stabilize product flow. The growing use of ready-to-eat foods, powdered mixes, spices, and baking ingredients by consumers demands that manufacturers use anti-caking agents to keep the product free-flowing and lump-free during storage and transportation. Additionally, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has guaranteed regulatory clarity, which promotes market development. The official definition of the anti-caking agents is provided in the 21 CFR 170.3(1) and states that they are substances in which the clumping of finely powdered or crystalline food products is prevented. There is also the trend of consumer awareness on food safety and clean label, which contributes to the market by compelling food producers to work with well-regulated, approved additives.
Moreover, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reported a total of 1,774.7 thousand as of June 2025 (seasonally adjusted) total employment in the food manufacturing sector (NAICS 311). This number indicates continuous demand and active production in the food industry of the U.S., which contributes to constant consumption of functional additives such as anti-caking agents. The production and nonsupervisory employees, in particular, amounted to 1,393.4 thousand in the same period. This increased the significance of the quality and stability of the product in extended distribution chains, and this further justifies the use of anti-caking agents in any industry.
Canada’s anti-caking agent market is likely to grow steadily over the forecast years by 2035, due to the growing food processing operations, new additive policy, and rising demand for quality powdered and granulated products. The chemical/ manufacturing industry in Canada demonstrates strong size as well as employment, which enhances the development of other related markets such as anti-caking agents. In 2022, the overall sales of the chemical industry in Canada amounted to CAD 72.7 billion, which represents an increase of approximately 30 percent as compared to 2019, when the country was not under COVID restrictions. The sales of industrial chemicals alone amounted to CAD $34.2 billion, which is only an increase of approximately 32% over 2019. In 2022, the sector itself provided 90,800 individuals with employment opportunities, and indirectly, another multiple of these via supply chain jobs and downstream customers. Additionally, the chemical manufacturing subsector contributes to the GDP of the province of Ontario, creating approximately $10 billion in 2023, and representing about 11.3% of the province, and employs approximately 56,300 people. These statistics suggest that there will be an increasing domestic demand for inputs like anti-caking agents (food, pharma, and industrial purposes) and production capacity.
Europe Market Insights
The European anti-caking agent market is likely to expand significantly over the projected years with a revenue share of 19.8%, owing to stringent regulations under strict food safety laws, primarily governed by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Additives such as silicon dioxide (E551) and ferrocyanides (E535, E536) are re-evaluated by EFSA to ascertain that they are safe to consumers provided appropriate limits are met. These caking inhibitors eliminate caking in powdered products like salt, spices, and protein products, and ensure the flowability of the products. The regulations of the European Union, such as Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2025/708, categorize substances under a technological additives category, and thus, their safety and effectiveness in feed and food applications are certain. Silicon dioxide, which is a common anti-caking agent, is regarded as safe with no reported acceptable daily intake, as it is not toxic. New issues on nanomaterials in calcium silicate and other additives are being researched in order to contain the threats.
Moreover, in the UK, the Food Standards Agency (FSA) keeps a list of approved additives and E numbers, so anti-caking agents are controlled by this agency to provide safety and transparency to consumers. The July 2025 guidance by FSA outlines the allowed additives in processed foods under stringent circumstances, which stabilize the market and quality of products. The Federal Institute of Risk Assessment (BfR) of Germany regulates the safety of food additives such as anti-caking agents through scientific evaluations and regulatory recommendations. Germany has adhered to EU standards, but it participates in risk assessments to promote safe usage in food items, especially focusing on the health of the consumer and environmental effects.