Aerospace Additive Manufacturing Market Outlook:
Aerospace Additive Manufacturing Market size was over USD 7.68 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 34.47 billion by 2035, growing at around 16.2% CAGR during the forecast period i.e., between 2026-2035. In the year 2026, the industry size of aerospace additive manufacturing is evaluated at USD 8.8 billion.
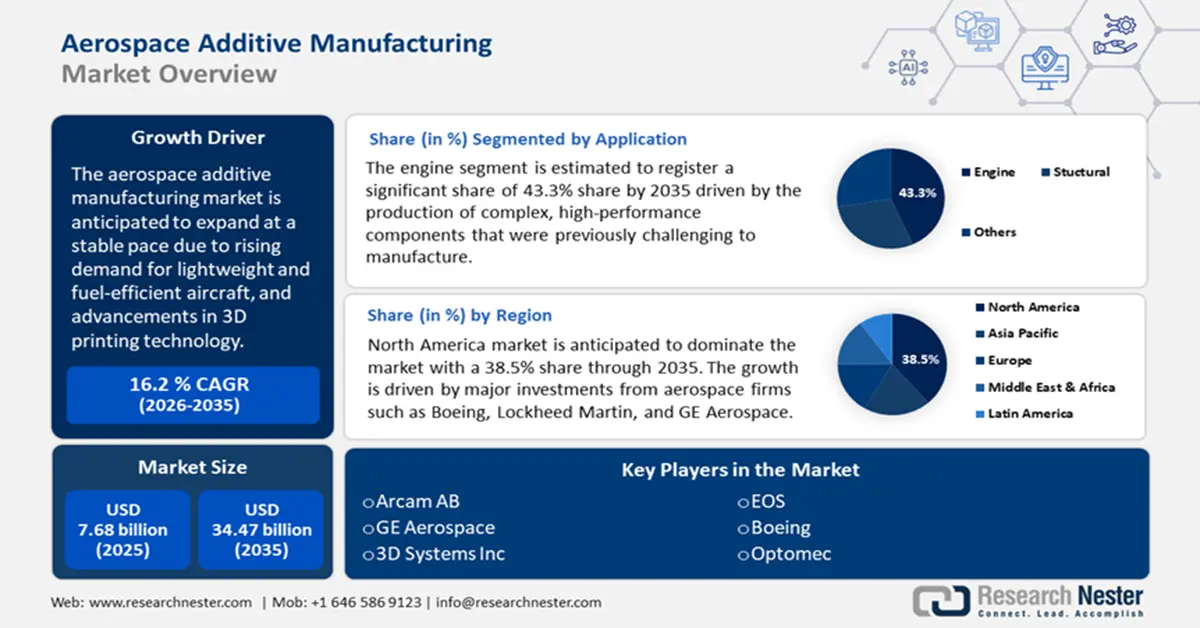
The primary growth driver of the aerospace additive manufacturing market is the rising demand for lightweight and fuel-efficient aircraft. Additive manufacturing allows for the production of lightweight components by using titanium and composite materials. Using these materials helps to build lighter aircraft leading to improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions. The U.S. Department of Energy states that replacing heavy steel components with high-strength steel, aluminum, or glass fiber-reinforced polymer composites can reduce component weight by 10-60%. Thus, the demand for lighter aircraft components to enhance fuel efficiency is a significant growth driver.
A key trend propelling the aerospace additive manufacturing market is the focus of aerospace companies on sustainable production to meet global emission regulations. This leads to a higher demand for additive manufacturing machines. Thus, the Observatory of Economic Complexity Report states that additive manufacturing machines were the world's 328th most traded product in 2022. It achieved a total trade of USD 12.1 billion. In addition to trade, the exports of additive manufacturing machines grew by 8.2%, from USD 11.2 billion to USD 12.1 billion in 2021 and 2022. Further, the trade in these machinery represented 0.051% of total world trade. The reduced material waste and lower energy consumption make additive manufacturing more environmentally friendly, driving the market growth.
Key Aerospace Additive Manufacturing Market Insights Summary:
Regional Highlights:
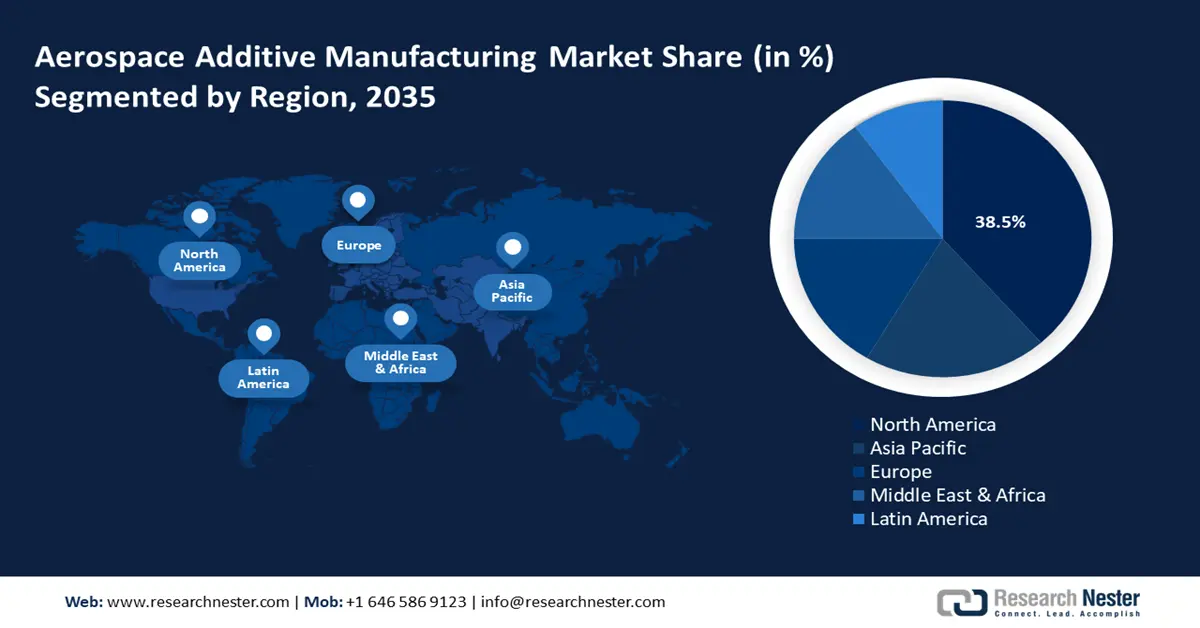
- North America commands a 38.5% share in the Aerospace Additive Manufacturing Market, driven by major aerospace investments and government support for additive manufacturing, ensuring strong growth through 2026–2035.
- The Asia Pacific Aerospace Additive Manufacturing Market is expected to grow rapidly through 2026–2035, attributed to rising air travel demand and indigenous aircraft programs.
Segment Insights:
- The Engine segment is expected to capture 43.3% market share by 2035, driven by additive manufacturing enabling complex, high-performance aerospace engine parts.
- The Spacecraft segment is projected to hold 71.50% market share by 2035, driven by demand for lightweight, cost-effective components.
Key Growth Trends:
- Advancements in 3D printing technology
- Increasing aerospace and defense investments
Major Challenges:
- High initial investment cost
- Certification and regulatory compliance
Key Players: GE Aerospace, 3D Systems Inc., CRP Technology SRL, Concept laser GMBH I, Eos, CRS Holdings Inc., Optomec, Stratasys Ltd.
Global Aerospace Additive Manufacturing Market Forecast and Regional Outlook:
Market Size & Growth Projections:
- 2025 Market Size: USD 7.68 billion
- 2026 Market Size: USD 8.8 billion
- Projected Market Size: USD 34.47 billion by 2035
- Growth Forecasts: 16.2% CAGR (2026-2035)
Key Regional Dynamics:
- Largest Region: North America (38.5% Share by 2035)
- Fastest Growing Region: Asia Pacific
- Dominating Countries: United States, Germany, United Kingdom, France, Japan
- Emerging Countries: China, India, Japan, South Korea, Singapore
Last updated on : 13 August, 2025
Aerospace Additive Manufacturing Market Growth Drivers and Challenges:
Growth Drivers
- Advancements in 3D printing technology: Advanced metal and polymer 3D printing techniques consist of selective laser melting (SLM) and electron beam melting (EBM). These techniques produce highly precise and accurate aerospace parts. Further, innovations in multi-material printing and hybrid manufacturing expand possibilities in 3D printing technology. Additive manufacturing creates intricate and lightweight structures that traditional methods cannot produce. In September 2024, SpaceX signed a 3D printing agreement of USD 8 million with Velo3D to enhance the role of additive manufacturing technology in the aerospace sector. This collaboration revolutionized the way spacecraft and rockets are designed, propelling the aerospace additive manufacturing market expansion.
- Increasing aerospace and defense investments: Governments and private aerospace companies are investing in additive manufacturing for military and commercial aircraft satellites and space exploration. The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD), NASA, Airbus, and Boeing are extensively using additive manufacturing for spacecraft components. For instance, in March 2024, GE Aerospace invested USD 650 million to enhance its manufacturing facilities across 14 U.S. states to increase production. Further, it also allocated more than USD 150 million for facilities running additive manufacturing equipment and USD 550 million for U.S. facilities and supplier partners. These investments in manufacturing facilities elevate the manufacturing process and support commercial and defense customers.
- Rising adoption in space exploration: Space missions require lightweight, strong, and customizable components in small production runs. 3D printing is used for rocket engines, satellite brackets, and space manufacturing. NASA, SpaceX, and Blue Origin use 3D printing for rocket engines, satellite components, and space habitats to reduce costs and improve performance. For instance, in January 2025, NASA developed a 3D-printed antenna in 2024 to provide a cost-effective solution for transmitting scientific data from space to earth. This antenna enhances communication capabilities for exploration missions. As space missions are extremely sensitive to weight, the use of advanced additive manufacturing maintains strength-to-weight ratios.
Challenges
- High initial investment cost: The cost of industrial-grade metal 3D printers, and aerospace certified materials equipment is very high. Thus, small and mid-sized aerospace firms struggle to afford technology, which limits adoption. Additionally, the limited availability of aerospace grade materials such as powders and polymers slows down material innovation and limits design flexibility for manufacturers.
- Certification and regulatory compliance: Aerospace components must meet extremely high safety and reliability standards set by FAA, EASA, NASA, and ASTM. The certification process for 3D printing parts is complex, and time consuming. Therefore, it is difficult for manufacturers to bring new components into commercial and military aircraft. Further, it slows down adoption, increases costs, and limits the use of additive manufacturing to non-critical parts. For instance, Boeing and Airbus have successfully introduced 3D-printed cabin and structural parts, but full-scale engine and fuselage adoption is still limited due to regulatory issues.
Aerospace Additive Manufacturing Market Size and Forecast:
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
|
CAGR |
16.2% |
|
Base Year Market Size (2025) |
USD 7.68 billion |
|
Forecast Year Market Size (2035) |
USD 34.47 billion |
|
Regional Scope |
|
Aerospace Additive Manufacturing Market Segmentation:
Application (Engine, Structural)
By 2035, engine aerospace additive manufacturing market is poised to capture over 43.3% revenue share. Additive manufacturing is transforming the aerospace engine sector by producing complex, high-performance components that were previously challenging to manufacture. Recent advancements have led to the successful integration of 3D-printed parts in aircraft engines to enhance design, efficiency, and performance. A notable development was the use of additive manufacturing technology by SpaceX in August 2024. The use of additive manufacturing by SpaceX simplified the Raptor 3 design. Additive manufacturing was used to produce complex components more efficiently which reduced part counts and improved engine performance. Additionally, modern aircraft engines now incorporate additive manufacturing produced components such as fuel nozzles, heat exchangers, sensor housings, and inducers. The growing role of additive manufacturing in aerospace propulsion systems leads to more efficient and reliable engines.
Platform (Spacecraft, Aircraft, and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles)
By the end of 2035, spacecraft segment is estimated to capture aerospace additive manufacturing market share of around 71.5%. The growth can be attributed to the need for light weight, high strength, and cost effective components for satellites, space probes, and crewed missions. Additive manufacturing in the aerospace sector enables the development of prototypes and complex spacecraft structures. The use of additive manufacturing reduces material waste and manufacturing time. Space agencies such as NASA, ESA, and JAXA along with Space X, Blue Origin, and Rocket Lab use additive manufacturing for engines, antennas, and in-space manufacturing systems.
Our in-depth analysis of the global aerospace additive manufacturing market includes the following segments:
|
Application |
|
|
Platform |
|
|
Technology |
|
|
Material |
|

Vishnu Nair
Head - Global Business DevelopmentCustomize this report to your requirements — connect with our consultant for personalized insights and options.
Aerospace Additive Manufacturing Market Regional Analysis:
North America Market Analysis
North America in aerospace additive manufacturing market is projected to dominate around 38.5% revenue share by the end of 2035. The region holds the largest market share which is driven by major investments from aerospace firms such as Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and GE Aerospace. The U.S. Department of Defense and NASA are leveraging additive manufacturing for lighter, more efficient aircraft and spacecraft components. Companies are increasingly using 3D printing for turbine parts, and structural components that help to improve performance and reduce costs. With ongoing advancements in metal additive manufacturing and government support, North America remains a global leader in aerospace 3D printing innovation. According to the European Patent Office Report, North America consists of the highest installations covering about 34.9% of all industrial additive manufacturing systems installed worldwide.
The U.S. aerospace additive manufacturing market is growing due to a rise in defense spending, demand for commercial aviation, and space exploration initiatives. Companies such as SpaceX and Relativity Space are pioneering fully 3D-printed rocket engines and launch vehicles reducing production time and costs. Further, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and the U.S. Department of Defense are accelerating additive manufacturing certification processes to enable wider adoption in military and civilian aircraft. With a strong hold of additive manufacturing startups, research institutions, and government support, it dominates the aerospace 3D printing innovation.
The aerospace additive manufacturing market in Canada is expanding driven by investments in research, sustainable aviation, and space technology. According to a 2024 report released by Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada, the aerospace industry in Canada is one of the most innovative and export-driven sectors contributing almost USD 28.9 billion to GDP and more than 218,000 jobs to the economy. Further, the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) is supporting additive manufacturing advancements through collaborations with industry leaders to develop next-gen aerospace materials. Moreover, Canada’s investment of USD 350 million to support its new Initiative for Sustainable Aviation Technology (INSAT) for the green industrial transformation also drives the aerospace industry. Furthermore, with a focus on lightweight design, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions, Canada is strengthening its role in aerospace 3D printing innovation.
Asia Pacific Market Analysis
Asia Pacific aerospace additive manufacturing market is expected to rise at a rapid pace through 2035, driven by rising air travel demand, indigenous aircraft programs, and space exploration efforts. India, China, and Japan are investing in additive manufacturing for next-generation fighter jets, commercial aircraft, and satellite production. Aerospace manufacturing firms AVIC and HAL India are integrating 3D printing to enhance aircraft performance and reduce production times. With government initiatives and increasing private sector involvement, Asia Pacific is emerging as a key player in the aerospace additive manufacturing market. The European Patent Office Report states that Asia Pacific accounts for 28.4% of additive manufacturing installations in the world.
The aerospace additive manufacturing market in China is expanding due to government-backed defense projects, commercial aviation growth, and space exploration initiatives. Companies in China are using additive manufacturing measures to develop fighter jet components, rocket engines, and spacecraft structures. Additionally, the European Patent Office Report suggests that China alone has a 10% share in total additive manufacturing system installations over the Asia Pacific. Further, the country’s Lunar and Mars missions are leveraging 3D printing to develop lightweight, high-strength parts to withstand the harsh conditions of deep space exploration. These advancements are bolstered by substantial state investments and advanced metal additive manufacturing technologies.
The aerospace additive manufacturing market in India is growing driven by indigenous defense programs, commercial aviation, and space research. The International Air Transport Association (IATA) states that India is expected to overtake China and the U.S. as the world's third-largest air passenger market by 2030. Organizations such as Hindustan Aeronautics Limited and ISRO are using additive manufacturing for fighter jet parts, rocket engines, and satellite components. Startups such as Skyroot Aerospace and Agnikul Cosmos are also advancing towards 3D printed rocket engines for cost effective launches. Additionally, with Make in India initiatives and private sector collaboration, India is advancing its aerospace additive manufacturing capabilities. The IBEF Report 2024 further suggests that due to rising demand in the aerospace sector in India, the number of airplanes is predicted to reach 2,200 by 2042. The rise in air travel directly influences the production of more aircraft which eventually leads to more use of aerospace additives while manufacturing.
Key Aerospace Additive Manufacturing Market Players:
- Arcam AB
- Company Overview
- Business Strategy
- Key Product Offerings
- Financial Performance
- Key Performance Indicators
- Risk Analysis
- Recent Development
- Regional Presence
- SWOT Analysis
- GE Aerospace
- 3D Systems Inc.
- CRP Technology SRL
- Concept laser GMBH I
- Eos
- CRS Holdings Inc.
- Optomec
- Stratasys Ltd
- Exone
- SLM solution group AG
Leading players dominating the aerospace additive manufacturing market include GE Aerospace, Boeing, and Airbus. These companies depend on additive manufacturing for engine components, structural parts, and fuel-efficient designs. Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman utilize additive manufacturing for hypersonic vehicles and satellites. Further, through continuous innovation and strategic partnerships, these companies shape the future of aerospace additive manufacturing. Here are some leading players in the aerospace additive manufacturing market:
Recent Developments
- In January 2025, EOS and 6K Additive received a USD 2.1 million grant for a sustainable additive manufacturing project. The project uses 6K Additive’s titanium powder, manufactured using its UniMelt microwave plasma reactors, which use over 73% less energy than conventional methods and produce 78% lower carbon emissions.
- In January 2024, Airbus developed the first metal 3D printer for space for the European Space Agency (ESA). It was tested at the International Space Station (ISS) Columbus which revolutionized the manufacturing process in space and future missions to the Moon.
- Report ID: 7221
- Published Date: Aug 13, 2025
- Report Format: PDF, PPT
- Explore a preview of key market trends and insights
- Review sample data tables and segment breakdowns
- Experience the quality of our visual data representations
- Evaluate our report structure and research methodology
- Get a glimpse of competitive landscape analysis
- Understand how regional forecasts are presented
- Assess the depth of company profiling and benchmarking
- Preview how actionable insights can support your strategy
Explore real data and analysis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Free Sample includes current and historical market size, growth trends, regional charts & tables, company profiles, segment-wise forecasts, and more.
Connect with our Expert
Copyright @ 2026 Research Nester. All Rights Reserved.




