Posted Date : 15 October 2025
Posted by : Shweta Singh
Electricity has been the foundation of modern civilization since its extensive adoption in the 19th and 20th centuries. From lighting homes to powering industries and enhancing the digital age, the role of electricity is evident. However, as the global call for energy rises and climate change concerns increase, the electricity sector is undergoing a seismic shift. The future of power is being constructed by the rapid transition from traditional fossil-fuel-based systems to more sustainable, decentralized, and intelligent electricity networks. This blog talks about the future of electricity, how it is generated, distributed, consumed, and managed. It examines the global energy transition, the rise of renewables, the evolution of smart grids, and the impact of emerging technologies on reshaping the world’s electricity landscape.
The Global Energy Shift: A Paradigm Shift
The 21st century marks a pivotal point in how energy is derived and consumed. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global electricity demand is expected to grow by 75% between 2020 and 2050, fueled by urbanization, population growth, and electrification of sectors of transportation and heating. Over the ages, coal, oil, and natural gas have dominated electricity generation. As of 2023, fossil fuels still accounted for around 61% of global electricity production, but this dominance is declining. The same IEA report highlights that renewables will account for nearly 90% of new electricity generation between now and 2050.
Underlying Trends Behind the Change
- Climate Change Policies: Governments are deploying stricter environmental regulations. Over 70 countries have committed to achieving net-zero emissions by mid-century, including the primary economies, namely the U.S., Europe, China, and India.
- Technological Advancements: Dropping prices of solar, wind, and battery storage solutions are making renewable sources of energy more viable.
- Investor Pressure: The Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) principles are impacting investment decisions, moving capital away from carbon-intensive assets.
- Consumer Awareness: Households and corporations are increasingly wanting clean energy options.
The Rise of Renewable Energy
Renewables, primarily solar and wind, are the backbone of the new electricity era. Their exponential growth has been remarkable, as reflected in the statistics given below.
- According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), solar PV capacity reached 1,350 GW and wind 1,020 GW by the end of 2023. Solar PV costs have dropped by 82% since 2010, and onshore wind costs by 39%, making them more competitive than fossil fuels in many regions.
- In 2023, renewables supplied 30% of the electricity worldwide, a figure expected to reach more than 60% by 2040.
The Rise of Energy Storage
To assure grid reliability, energy storage, particularly batteries, is becoming crucial. Battery storage capacity rose by 75% globally in 2023, with China and the U.S. leading the way.
- The global battery storage market is projected to grow from 17 GW in 2023 to over 420 GW by 2030
- Innovations like lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) batteries and solid-state batteries are pushing the boundaries of storage technology.
- Pumped hydro and green hydrogen also provide long-duration storage options, important for balancing seasonal variations in renewable output.
Electrification of Transport and Industry
Electricity is now powering sectors that were earlier dependent on fossil fuels.
Transportation:
- Electric vehicle sales topped 14 million units in 2023, accounting for 18% of total car sales globally.
- According to the IEA Global EV Outlook, EVs could hold about 60% of new car sales by 2030.
- Charging infrastructure and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies are advancing to merge EVs into the power grid dynamically.
Industry and Buildings:
- Electrification of industrial processes such as steelmaking, chemical production, and HVAC systems is advancing rapidly.
- Heat pumps, already widely prevalent in Europe, are becoming the standard in many regions, substituting fossil-fuel-based heating.
Smart Grids and Decentralized Energy Systems
Traditional electricity systems were built for one-way power flow from large, centralized power plants to consumers. The future grid, however, is smart, digital, and two-way.
Core Technologies Driving Smart Grids
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): Allows real-time data collection and pricing.
- Distributed Energy Resources (DERs): This consists of rooftop solar, microgrids, and community batteries.
- Grid Automation: AI and IoT systems enhance load balancing, fault detection, and demand response. According to Research Nester, the smart grid market is projected to rise from $50 billion in 2023 to $150 billion by 2030. Decentralization also empowers prosumers, i.e., consumers who produce their own power. In Germany, more than 2 million homes had rooftop solar in 2023, contributing meaningfully to the national energy supply.
Digitalization and the Role of AI in Energy
The incorporation of digital technologies is changing how electricity systems are monitored, managed, and upgraded.
- Artificial intelligence is used for predictive maintenance, grid forecasting, and optimizing energy trading.
- Blockchain is facilitating peer-to-peer electricity trading and decentralized energy marketplaces.
- Digital twins of power plants and grids allow real-time simulation and efficient decision-making.
Global Trends and Regional Analysis
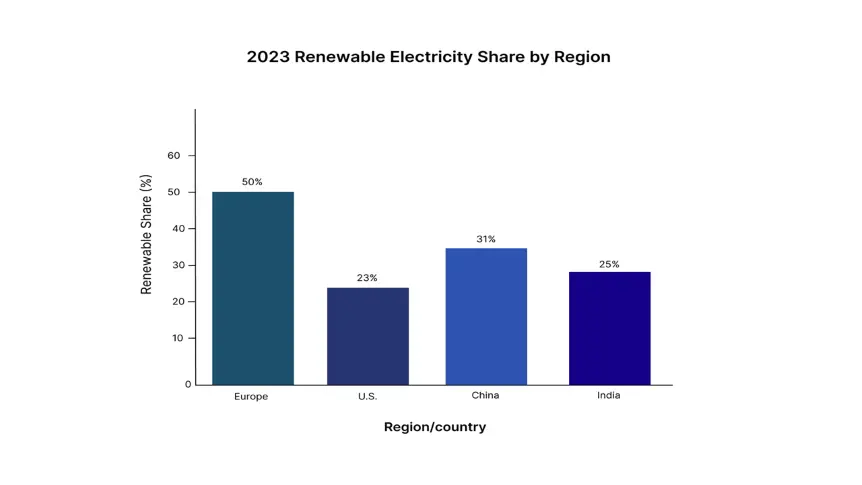
- Europe: Europe leads the global energy transition, driven by progressive climate legislation, ambitious renewable energy targets, and strong public support for sustainable development. The European Green Deal, introduced in December 2019, sets a legally binding goal of achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. The intermediate target is to reduce emissions by at least 55% by 2030, compared to 1990 levels. According to the European Environment Agency (EEA), as of 2023, renewables contributed 50.5% of the European Union's electricity generation. Wind (17.5%) and solar (8.5%) are leading the charge.
- United States: The U.S. is undergoing a transformative shift in its energy infrastructure, supported by federal legislation and private sector innovation. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), passed in August 2022, earmarks $370 billion for clean energy investment over a decade. This includes $60 billion in clean energy manufacturing, $30 billion in production tax credits for solar panels, wind turbines, and batteries, and $7,500 tax credits for new electric vehicles (EVs)
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), solar and wind combined accounted for 23.1% of total electricity generation in 2023, up from 18.2% in 2020. Additionally, Texas, once known for oil, became the leading U.S. state for wind generation (37% of the state’s electricity), followed by solar growth in California and Arizona. The EIA projects that renewables will overtake natural gas as the primary source of electricity generation in the U.S. by 2030, reaching a 44% share. - China: China is the world’s largest emitter of CO₂, and also the undisputed global leader in renewable energy deployment, manufacturing, and investment. As per China’s National Energy Administration, the country added an unprecedented 210 GW of new renewable energy capacity in 2023 alone, more than the entire installed capacity of many developed nations. This included 113 GW of solar PV and 76 GW of wind power. By the end of 2023, China’s total installed renewable capacity reached 1,400 GW, comprising 610 GW solar, 430 GW wind, and 400 GW hydroelectric.
In 2020, China announced its goal to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 and peak emissions by 2030. To support this, the country aims to have 80% of its electricity from non-fossil fuel sources by 2060, with interim goals of 50% by 2030. China also dominates global clean energy manufacturing with 80% of global solar panel production, 60% of wind turbine components, and 75% of lithium-ion battery production - India: India, the world’s third-largest energy consumer, is emerging as a major player in the clean energy transition, balancing economic development with sustainability. India aims to install 500 GW of non-fossil fuel electricity capacity by 2030, as per its Updated Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) under the Paris Agreement. According to the Ministry of Power, more than 99.9% of villages have been electrified, and efforts are ongoing to ensure 24x7 power access to all households. India has also launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission in 2023, targeting 5 MMT (Million Metric Tons) of green hydrogen annual production capacity by 2030 and associated renewable energy capacity of 125 GW.
The Hydrogen Economy: A Future Pillar?
Green hydrogen, produced via electrolysis powered by renewables, offers a clean energy vector for sectors hard to electrify, like heavy industry and aviation. The global green hydrogen market is expected to grow from $4 billion in 2023 to $130 billion by 2030, according to Research Nester. The key initiatives generally consist of Germany’s National Hydrogen Strategy, India’s Green Hydrogen Mission, and Australia’s H2-Hub projects. In addition, hydrogen serves as a long-term energy storage solution and supports grid stability.
Energy Transition 2050: What Lies Ahead?
The electricity sector of the future generation will be:
- Clean: Led by solar, wind, hydro, and nuclear power with low carbon emissions.
- Smart: AI-driven systems will predict demand, detect faults, and automate trading.
- Decentralized: Communities and businesses will produce and store their power.
- Flexible: Energy will flow in multiple directions, adjusting to supply and demand in real-time.
Conclusion
The future of electricity is going through a radical and necessary transformation. As the world races to decarbonize and digitize, electricity will sit at the core of a sustainable and inclusive energy ecosystem. While challenges persist, the amalgamation of policy, technology, and consumer awareness is setting the stage for a stable and cleaner power future. Investments in renewable energy, grid modernization, and digital innovation will define how well the transition is managed. Governments, businesses, and individuals must work collaboratively to build a power system that is efficient, reliable, and environmentally sound.
Contact Us







